Introduction¶
LaminDB is an open-source data framework to make computational biology more robust, scalable, and understandable. It provides a queryable lakehouse, tracks data sources & transformations, offers data curation & transfer tools, and helps managing experimental metadata and ontologies. Datasets, models, and code in LaminDB are findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR).
Why?

In many organizations, biological datasets are mismanaged, not queryable, and not standardized. It’s often difficult to reproduce analytical results or understand how a dataset was processed. It’s typically hard to train models on historical data, orthogonal assays, or datasets generated by other teams.
Datasets have so far been managed with versioned storage systems (file systems, object storage, git, dvc), GUI-focused community or SaaS platforms, structureless data lakes, rigid data warehouses (SQL, monolithic arrays), and data lakehouses for tabular data.
LaminDB goes beyond these systems with a lakehouse that models biological data objects beyond tables with enough structure to enable queries and enough freedom to keep the pace of R&D high.
For data objects like DataFrame, AnnData, .zarr, .tiledbsoma, etc., LaminDB tracks and provides the rich context that collaborative biological research requires:
data lineage: data sources and transformations; scientists and machine learning models
domain knowledge and experimental metadata: the features and labels derived from domain entities
data curation: validation, standardization, and annotation
data transfer: simple sharing of datasets with their metadata context
In this blog post, we discuss a breadth of data management problems of the field.
LaminDB specs
Any LaminDB instance comes with an underlying SQL metadata database to organize files, folders, and arrays across any number of storage locations.
The following detailed specs are for the Python package lamindb. For the analogous R package laminr, see the R docs.
Manage data & metadata with a unified API (“lakehouse”).
Model important entities as an ORM which their own metadata registry:
RecordModel files and folders as datasets & models via one class:
ArtifactManage features & labels:
Feature,FeatureSet,ULabelPlug-in custom schemas & manage schema migrations
Use array formats in memory & storage: DataFrame, AnnData, MuData, SOMA, … backed by parquet, zarr, TileDB, HDF5, h5ad, DuckDB, …
Create iterable collections of artifacts with data loaders:
CollectionVersion artifacts, collections & transforms:
IsVersioned
Track data lineage across notebooks, scripts, pipelines & UI.
Track run context with a simple method call:
track()A unified registry for all your notebooks, scripts & pipelines:
TransformA unified registry for all data transformation runs:
RunManage execution reports, source code and Python environments for notebooks & scripts
Integrate with workflow managers: redun, nextflow, snakemake
Manage registries for experimental metadata & in-house ontologies, import public ontologies.
Use >20 public ontologies with plug-in
bionty:Gene,Protein,CellMarker,ExperimentalFactor,CellType,CellLine,Tissue, …Safeguards against typos & duplications
Version ontology
Validate, standardize & annotate.
Validate & standardize metadata:
validate,standardize.High-level curation flow including annotation:
CuratorInspect validation failures:
inspect
Organize and share data across a mesh of LaminDB instances.
Create & load instances like git repos:
lamin init&lamin loadZero-copy transfer data across instances
Integrate with analytics tools.
Vitessce:
save_vitessce_config
Zero lock-in, scalable, auditable.
Zero lock-in: LaminDB runs on generic backends server-side and is not a client for “Lamin Cloud”
Flexible storage backends (local, S3, GCP, anything fsspec supports)
Two SQL backends for managing metadata: SQLite & Postgres
Scalable: metadata registries support 100s of millions of entries, storage is as scalable as S3
Auditable: data & metadata records are hashed, timestamped, and attributed to users (full audit log to come)
Secure: embedded in your infrastructure (Lamin has no access to your data & metadata)
Tested, typed, idempotent & ACID
LaminHub is a data collaboration hub built on LaminDB similar to how GitHub is built on git.
LaminHub overview
See for yourself by browsing the demo instances in the hub UI or lamin connect owner/instance them via the CLI.
lamin.ai/laminlabs/lamindata - A generic demo instance with various data types
lamin.ai/laminlabs/cellxgene - An instance that interfaces the CELLxGENE data (guide)
lamin.ai/laminlabs/arrayloader-benchmarks - Work with ML models & benchmarks
See the pricing page. Basic LaminHub features are free.
Secure & intuitive access management.
Rather than configuring storage & database permissions directly on AWS or GCP, LaminHub allows you to manage collaborators for databases & storage locations in the same way you manage access to repositories on GitHub. See Access management.
A UI to work with LaminDB instances.
See an overview of all datasets, models, code, and metadata in your instance.
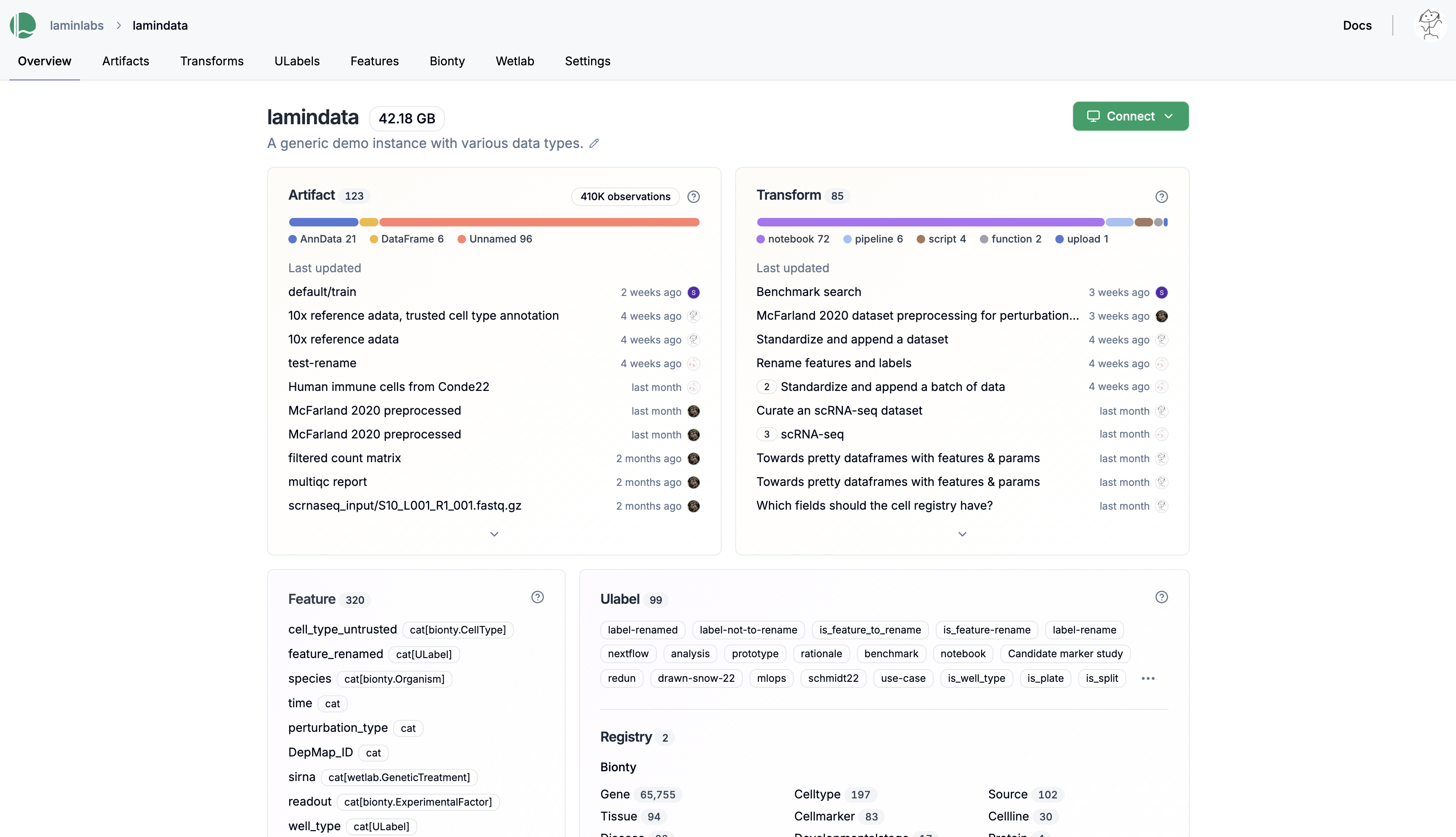
See validated datasets in context of ontologies & experimental metadata.
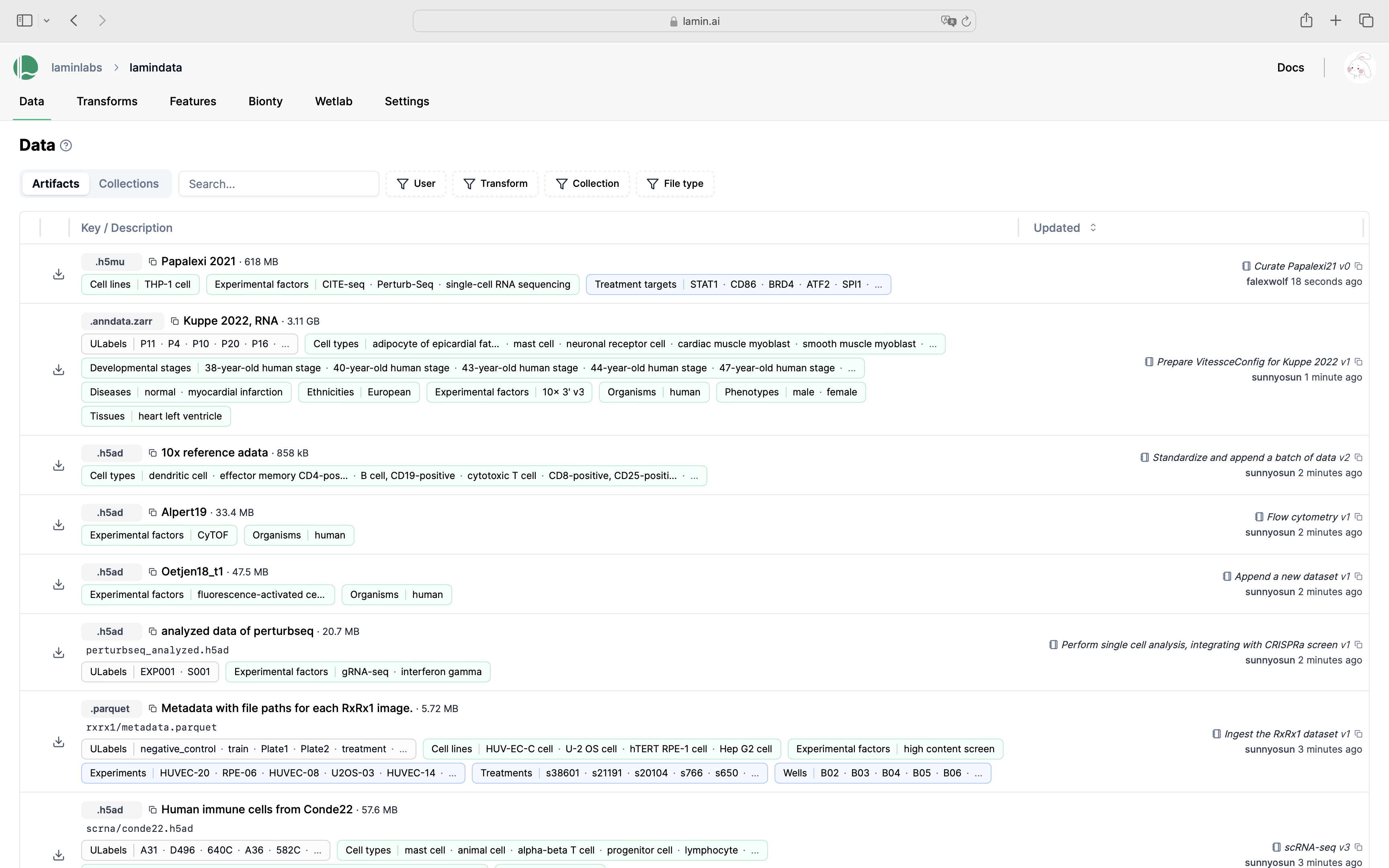
Query & search.
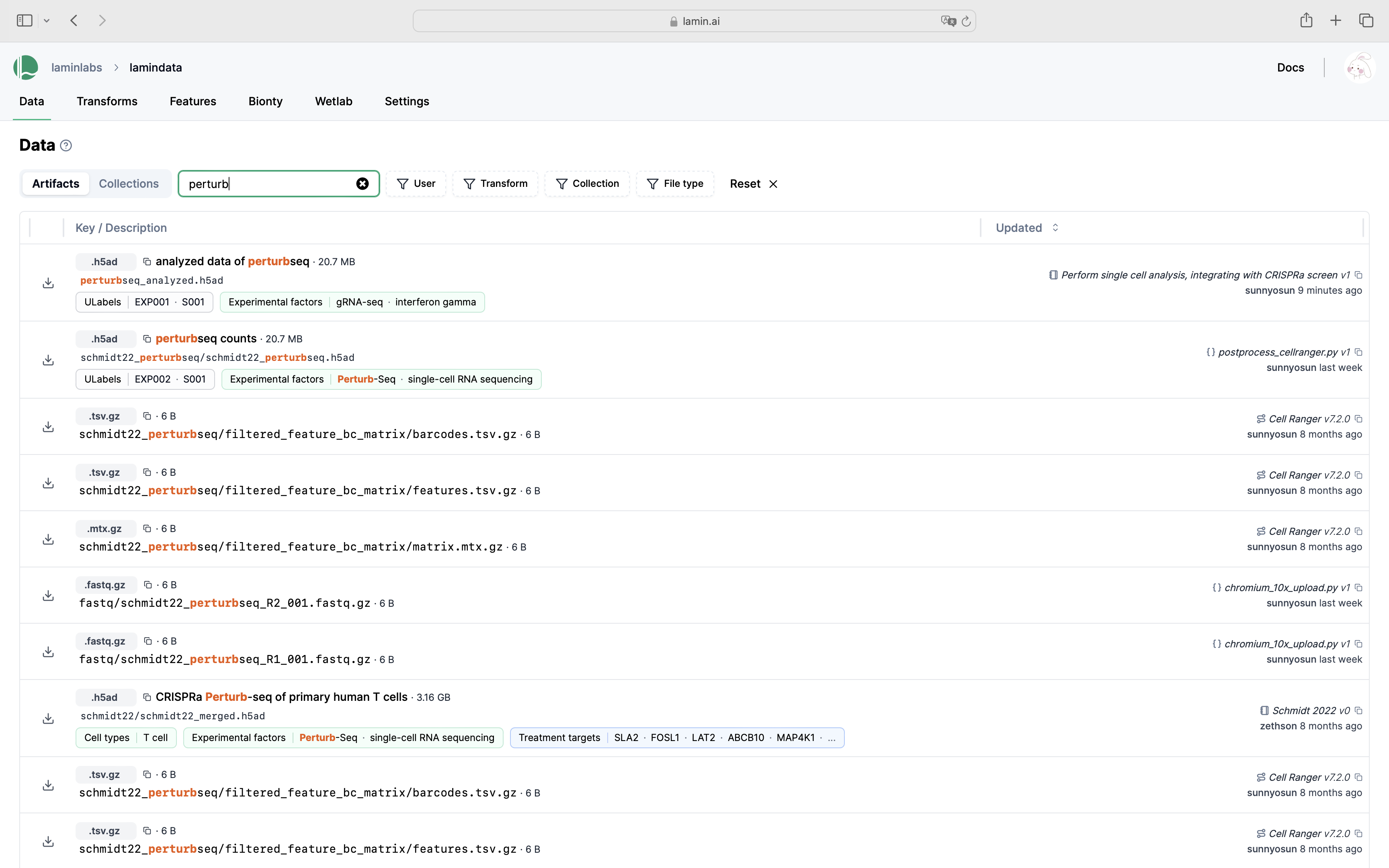
See scripts, notebooks & pipelines with their inputs & outputs.

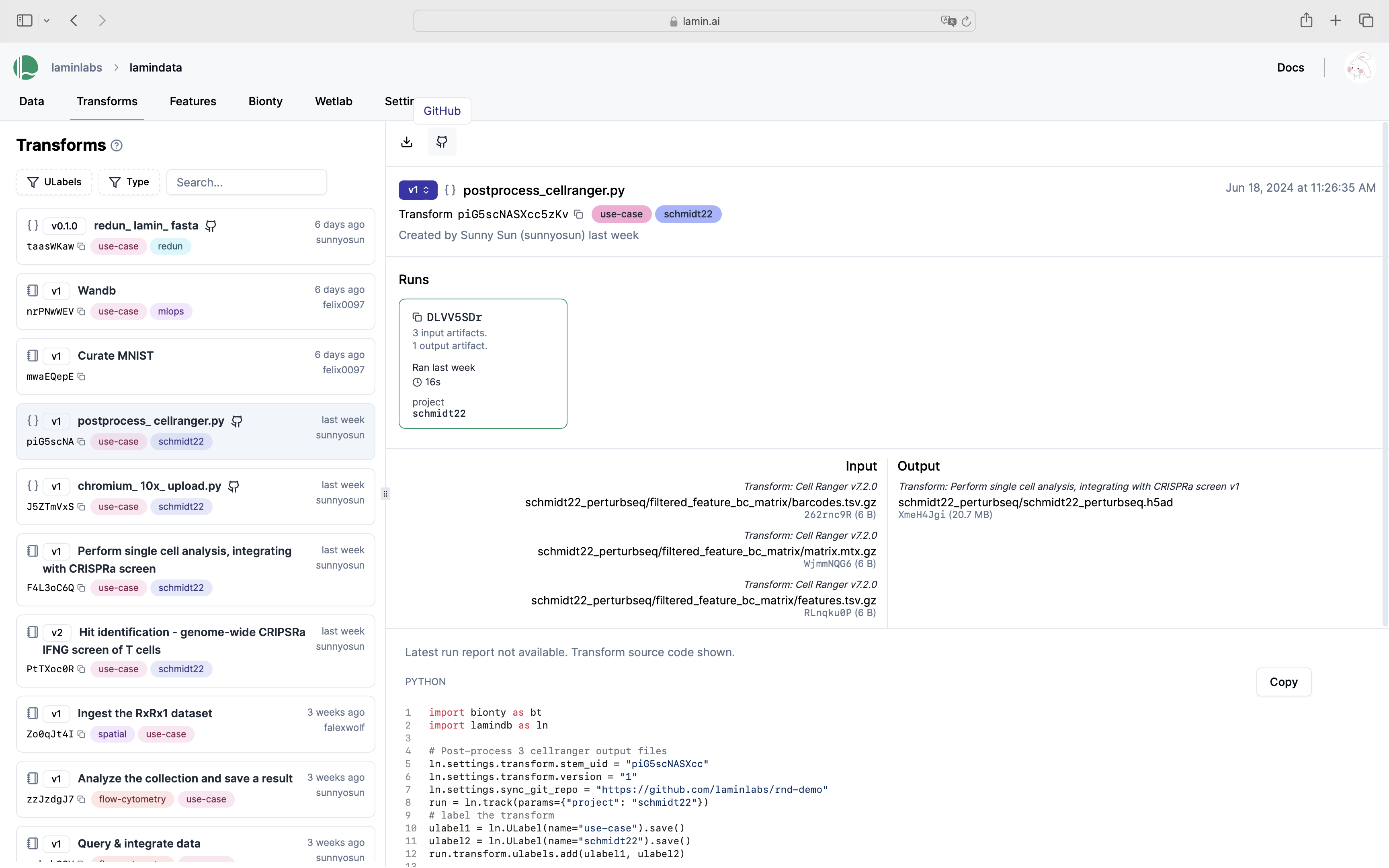
Track pipelines, notebooks & UI transforms in one place.
Quickstart¶
Install the lamindb Python package.
# install with support for notebooks, biological entities & AWS
pip install 'lamindb[jupyter,bionty,aws]'
Connect to a LaminDB instance.
lamin connect account/instance # <-- replace with your instance
Access an input dataset and save an output dataset.
import lamindb as ln
ln.track() # track a run for a notebook or script
artifact = ln.Artifact.get("3TNCsZZcnIBv2WGb0001") # get an artifact record by uid
artifact.describe() # show metadata of artifact
df = artifact.load() # load the artifact into memory, e.g., a DataFrame
# do your work
ln.Artifact("./my_result_folder", description="My result").save() # save a folder
ln.finish() # mark the run as finished
# laminr needs pip install 'lamindb[aws]'
install.packages("laminr", dependencies = TRUE) # install the laminr package from CRAN
library(laminr)
db <- connect() # connect to the instance you configured on the terminal
db$track() # track a run of your notebook or script
artifact <- db$Artifact$get("3TNCsZZcnIBv2WGb0001") # get an artifact record by uid
df <- artifact$load() # load the artifact into memory, e.g., a DataFrame
# do your work
db$Artifact.from_path("./my_result_folder", description="My result").save() # save a folder
db$finish() # mark the run finished
Save an html export for .qmd or .Rmd file as a report.
lamin save my-analysis.Rmd
For more, see the R docs.
Concepts¶
LaminDB instance¶
A LaminDB instance is a single relational database that manages metadata for datasets across any number of storage locations, conforming to LaminDB’s schema management. You can readily create a local instance to manage data in a local folder.
Here, you create one that mounts schema module bionty.
# manage artifacts in local directory `./lamin-intro`
!lamin init --storage ./lamin-intro --schema bionty
Show code cell output
! using anonymous user (to identify, call: lamin login)
→ connected lamindb: anonymous/lamin-intro
You can also connect your cloud storage locations (S3, GCP, R2, HuggingFace, etc.) and databases (Postgres & SQLite). See Install & setup. If you decide to connect your LaminDB instance to LaminHub, you will see data & metadata in a GUI.

Data transformation¶
A data transformation (a “transform”) is any piece of code (script, notebook, pipeline, function) that can be applied to input data to produce output data.
When you call track(), you register a transform in the Transform registry, starting to auto-track inputs and outputs, with each run stored in Run.
import lamindb as ln
# --> `ln.track()` generates a uid for your code
# --> `ln.track(uid)` initiates a tracked run
ln.track("FPnfDtJz8qbE0000")
Show code cell output
→ connected lamindb: anonymous/lamin-intro
→ created Transform('FPnfDtJz'), started new Run('T2rAm3yf') at 2024-12-21 08:21:38 UTC
→ notebook imports: anndata==0.11.1 bionty==0.53.2 lamindb==0.77.3 pandas==2.2.3 pytest==8.3.4
Is this compliant with OpenLineage?
Yes. What OpenLineage calls a “job”, LaminDB calls a “transform”. What OpenLineage calls a “run”, LaminDB calls a “run”.
What is the uid?
To tie a piece of code to a record in a database in a way that survives name and content changes, you need to attach it to an immutable identifier, e.g., LaminDB’s uid.
git, by comparison, identifies code by its content hash & file name. If you rename a notebook or script file and change the content, you lose the identity of the file.
To version transforms, LaminDB generates uid = f"{stem_uid}{version_suffix}" so that different versions of a transform are grouped by a “stem uid” while the last four uid characters encoding its version. All versioned entities in LaminDB are versioned in this way, including artifacts and collections.
Artifact¶
An Artifact stores a dataset or model as a file, folder or array.
import pandas as pd
# a sample dataset
df = pd.DataFrame(
{"CD8A": [1, 2, 3], "CD4": [3, 4, 5], "CD14": [5, 6, 7], "perturbation": ["DMSO", "IFNJ", "DMSO"],},
index=["sample1", "sample2", "sample3"],
)
# create & save an artifact from a DataFrame -- delete via artifact.delete(permanent=True)
artifact = ln.Artifact.from_df(df, description="my RNA-seq").save()
# describe the artifact
artifact.describe()
Show code cell output
Artifact .parquet/DataFrame └── General ├── .uid = 'x4GHQn89scew7XQt0000' ├── .size = 3638 ├── .hash = 'WRA-eosPpImwftGEDTXwkw' ├── .path = /home/runner/work/lamin-docs/lamin-docs/docs/lamin-intro/.lamindb/x4GHQn89scew7XQt0000.parquet ├── .created_by = anonymous ├── .created_at = 2024-12-21 08:21:38 └── .transform = 'Introduction'
Load the artifact into memory.
artifact.load()
| CD8A | CD4 | CD14 | perturbation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sample1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | DMSO |
| sample2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | IFNJ |
| sample3 | 3 | 5 | 7 | DMSO |
View data lineage.
artifact.view_lineage()
How do I create an artifact for a file or folder?
Source path is local:
ln.Artifact("./my_data.fcs", description="my flow cytometry file")
ln.Artifact("./my_images/", description="my folder of images")
Upon artifact.save(), the source path will be copied or uploaded into your instance’s current default storage.
If the source path is remote or already in a registered storage location, artifact.save() won’t trigger data duplication but register the existing path.
ln.Artifact("s3://my-bucket/my_data.fcs", description="my flow cytometry file")
ln.Artifact("s3://my-bucket/my_images/", description="my folder of images")
You can also use other remote file systems supported by `fsspec`.
How does LaminDB compare to a AWS S3?
LaminDB provides a relational metadata layer on top of AWS S3 (or GCP storage, file system, etc.).
Similar to organizing files in file systems & object stores with paths, you can organize artifacts using the key parameter of Artifact.
However, LaminDB encourages you to not rely on semantic keys but instead organize your data based on metadata.
Rather than memorizing names of folders and files, you find data via the entities you care about: people, code, experiments, genes, proteins, cell types, etc.
LaminDB indexes artifacts in storage via the uid.
This scales much better than semantic keys, which lead to deep hierarchical information structures that can become hard to navigate.
Because metadata is typed and relational, you can work with more structure, more integrity, and richer queries compared to leveraging S3’s JSON-like metadata. You’ll learn more about this below.
Are artifacts aware of array-like data?
Yes.
You can make artifacts from paths referencing array-like objects:
ln.Artifact("./my_anndata.h5ad", description="curated array")
ln.Artifact("./my_zarr_array/", description="my zarr array store")
Or from in-memory objects:
ln.Artifact.from_df(df, description="my dataframe")
ln.Artifact.from_anndata(adata, description="annotated array")
You can open large artifacts for slicing from the cloud or load small artifacts directly into memory.
Just like transforms, artifacts are versioned. Let’s create a new version by revising the dataset.
# keep the dataframe with a typo around - we'll need it later
df_typo = df.copy()
# fix the "IFNJ" typo
df.loc["sample2", "perturbation"] = "IFNG"
# create a new version by revising the artifact
artifact = ln.Artifact.from_df(df, revises=artifact).save()
# see all versions of an artifact
artifact.versions.df()
Show code cell output
| uid | key | description | suffix | type | size | hash | n_objects | n_observations | _hash_type | _accessor | visibility | _key_is_virtual | storage_id | transform_id | version | is_latest | run_id | created_at | created_by_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | x4GHQn89scew7XQt0000 | None | my RNA-seq | .parquet | dataset | 3638 | WRA-eosPpImwftGEDTXwkw | None | None | md5 | DataFrame | 1 | True | 1 | 1 | None | False | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:38.914498+00:00 | 1 |
| 2 | x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001 | None | my RNA-seq | .parquet | dataset | 3638 | PE7xGyIgaqxqJ56hf5ZzVQ | None | None | md5 | DataFrame | 1 | True | 1 | 1 | None | True | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:39.029368+00:00 | 1 |
I’d rather control versioning through a key or file path like on S3.
That works, too, and you won’t need to pass an old version via revises:
artifact_v1 = ln.Artifact.from_df(df, key="my_datasets/my_study1.parquet").save()
# below automatically creates a new version of artifact_v1 because the `key` matches
artifact_v2 = ln.Artifact.from_df(df_updated, key="my_datasets/my_study1.parquet").save()
The good thing about passing revises: Artifact is that it works for entities that don’t come with a file path and you don’t need to worry about coming up with naming conventions for paths.
You’ll see that LaminDB makes it easy to organize data by entities, rather than file paths.
Label¶
Label an artifact with a ULabel and a bionty.CellType. The same works for any entity in any custom schema module.
import bionty as bt
# create & save a ulabel record
candidate_marker_study = ln.ULabel(name="Candidate marker study").save()
# label the artifact
artifact.ulabels.add(candidate_marker_study)
# repeat for a bionty entity
cell_type = bt.CellType.from_source(name="effector T cell").save()
artifact.cell_types.add(cell_type)
# describe the artifact
artifact.describe()
Show code cell output
Artifact .parquet/DataFrame ├── General │ ├── .uid = 'x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001' │ ├── .size = 3638 │ ├── .hash = 'PE7xGyIgaqxqJ56hf5ZzVQ' │ ├── .path = /home/runner/work/lamin-docs/lamin-docs/docs/lamin-intro/.lamindb/x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001.parquet │ ├── .created_by = anonymous │ ├── .created_at = 2024-12-21 08:21:39 │ └── .transform = 'Introduction' └── Labels └── .cell_types bionty.CellType effector T cell .ulabels ULabel Candidate marker study
Registry¶
LaminDB’s central classes are registries that store records (Record objects).
We’ve already seen how to create new artifact, transform and ulabel records.
The easiest way to see the latest records of a given type is to call the class method df.
ln.ULabel.df()
Show code cell output
| uid | name | description | reference | reference_type | run_id | created_at | created_by_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | ||||||||
| 1 | lBE1zTbV | Candidate marker study | None | None | None | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:39.049410+00:00 | 1 |
Existing records are stored in the record’s registry (metaclass Registry), which maps 1:1 to a SQL table.
A record and its registry share the same fields, which define the metadata you can query for. If you want to see them, look at the class or auto-complete.
ln.Artifact
Show code cell output
Artifact
Simple fields
.uid: CharField
.key: CharField
.description: CharField
.suffix: CharField
.type: CharField
.size: BigIntegerField
.hash: CharField
.n_objects: BigIntegerField
.n_observations: BigIntegerField
.visibility: SmallIntegerField
.version: CharField
.is_latest: BooleanField
.created_at: DateTimeField
.updated_at: DateTimeField
Relational fields
.storage: Storage
.transform: Transform
.run: Run
.created_by: User
.ulabels: ULabel
.input_of_runs: Run
.feature_sets: FeatureSet
.collections: Collection
Bionty fields
.organisms: bionty.Organism
.genes: bionty.Gene
.proteins: bionty.Protein
.cell_markers: bionty.CellMarker
.tissues: bionty.Tissue
.cell_types: bionty.CellType
.diseases: bionty.Disease
.cell_lines: bionty.CellLine
.phenotypes: bionty.Phenotype
.pathways: bionty.Pathway
.experimental_factors: bionty.ExperimentalFactor
.developmental_stages: bionty.DevelopmentalStage
.ethnicities: bionty.Ethnicity
Query & search¶
You can write arbitrary relational queries using the class methods get and filter.
The syntax for it is Django’s query syntax, one of the two most popular ORMs in Python (the other is SQLAlchemy).
# get a single record by uid (here, the latest version of the current notebook)
transform = ln.Transform.get("FPnfDtJz8qbE")
# get a single record by matching a field
transform = ln.Transform.get(name="Introduction")
# get a set of records by filtering on description
ln.Artifact.filter(description="my RNA-seq").df()
# query all artifacts ingested from the current notebook
artifacts = ln.Artifact.filter(transform=transform).all()
# query all artifacts ingested from a notebook with "intro" in the name and labeled "Candidate marker study"
artifacts = ln.Artifact.filter(
transform__name__icontains="intro", ulabels=candidate_marker_study
).all()
The class methods search and lookup help finding sets of approximately matching records.
# search in a registry
ln.Transform.search("intro").df()
# look up records with auto-complete
ulabels = ln.ULabel.lookup()
cell_types = bt.CellType.lookup()
Show me a screenshot
Feature¶
What fields are to metadata records, features are to datasets. You can annotate datasets by the features they measure.
But because LaminDB validates all user input against its registries, annotating with a "temperature" feature doesn’t work right away.
import pytest
with pytest.raises(ln.core.exceptions.ValidationError) as e:
artifact.features.add_values({"temperature": 21.6})
print(e.exconly())
Show code cell output
lamindb.core.exceptions.ValidationError: These keys could not be validated: ['temperature']
Here is how to create a feature:
ln.Feature(name='temperature', dtype='float').save()
Following the hint in the error message, create & save a Feature.
# define the "temperature" feature
ln.Feature(name="temperature", dtype="float").save()
# now we can annotate with the feature & the value
artifact.features.add_values({"temperature": 21.6})
# describe the artifact
artifact.describe()
Show code cell output
Artifact .parquet/DataFrame ├── General │ ├── .uid = 'x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001' │ ├── .size = 3638 │ ├── .hash = 'PE7xGyIgaqxqJ56hf5ZzVQ' │ ├── .path = /home/runner/work/lamin-docs/lamin-docs/docs/lamin-intro/.lamindb/x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001.parquet │ ├── .created_by = anonymous │ ├── .created_at = 2024-12-21 08:21:39 │ └── .transform = 'Introduction' ├── Linked features │ └── temperature float 21.6 └── Labels └── .cell_types bionty.CellType effector T cell .ulabels ULabel Candidate marker study
We can also annotate with categorical features:
# define a categorical feature
ln.Feature(name="study", dtype="cat").save()
# add a categorical value
artifact.features.add_values({"study": "Candidate marker study"})
# describe the artifact with type information
artifact.describe()
Show code cell output
Artifact .parquet/DataFrame ├── General │ ├── .uid = 'x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001' │ ├── .size = 3638 │ ├── .hash = 'PE7xGyIgaqxqJ56hf5ZzVQ' │ ├── .path = /home/runner/work/lamin-docs/lamin-docs/docs/lamin-intro/.lamindb/x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001.parquet │ ├── .created_by = anonymous │ ├── .created_at = 2024-12-21 08:21:39 │ └── .transform = 'Introduction' ├── Linked features │ └── study cat[ULabel] Candidate marker study │ temperature float 21.6 └── Labels └── .cell_types bionty.CellType effector T cell .ulabels ULabel Candidate marker study
This is how you query artifacts by features.
ln.Artifact.features.filter(study__contains="marker study").df()
Show code cell output
| uid | key | description | suffix | type | size | hash | n_objects | n_observations | _hash_type | _accessor | visibility | _key_is_virtual | storage_id | transform_id | version | is_latest | run_id | created_at | created_by_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001 | None | my RNA-seq | .parquet | dataset | 3638 | PE7xGyIgaqxqJ56hf5ZzVQ | None | None | md5 | DataFrame | 1 | True | 1 | 1 | None | True | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:39.029368+00:00 | 1 |
Features organize labels by how they’re measured in datasets, independently of how labels are stored in metadata registries.
Key use cases¶
Understand data lineage¶
Understand where a dataset comes from and what it’s used for (background).
artifact.view_lineage()

I just want to see the transformations.
transform.view_lineage()

You don’t need a workflow manager to track data lineage (if you want to use one, see Pipelines – workflow managers). All you need is:
import lamindb as ln
ln.track() # track your run
# your code
ln.finish() # mark run as finished, save execution report, source code & environment
Below is how a single transform (a notebook) with its run report looks on the hub.

To create a new version of a notebook or script, run lamin load on the terminal, e.g.,
$ lamin load https://lamin.ai/laminlabs/lamindata/transform/13VINnFk89PE0004
→ connected lamindb: laminlabs/lamindata
→ updated uid: 13VINnFk89PE0004 → 13VINnFk89PE0005
→ notebook is here: mcfarland_2020_preparation.ipynb
Curate datasets¶
In the quickstart, you just saw how to ingest & annotate datasets without validation. This is often enough if you’re prototyping or working with one-off studies. But if you want to create a big body of standardized data, you have to invest the time to curate your datasets.
Let’s use a Curator object to curate a DataFrame.
# construct a Curator object to validate & annotate a DataFrame
curator = ln.Curator.from_df(
df,
# define validation criteria as mappings
columns=ln.Feature.name, # map column names
categoricals={"perturbation": ln.ULabel.name}, # map categories
)
# validate the dataset
curator.validate()
Show code cell output
✓ added 1 record with Feature.name for "columns": 'perturbation'
• mapping "perturbation" on ULabel.name
! 2 terms are not validated: 'DMSO', 'IFNG'
→ fix typos, remove non-existent values, or save terms via .add_new_from("perturbation")
False
The validation did not pass because LaminDB’s registries don’t yet know about the features "CD8A", "CD4", "CD14", "perturbation" and labels "DMSO", "IFNG", "DMSO" in this dataset.
Hence, we need to initially populate them.
# add non-validated features based on the DataFrame columns
curator.add_new_from_columns()
# add non-validated labels based on the perturbation column of the dataframe
curator.add_new_from("perturbation")
# see the updated content of the ULabel registry
ln.ULabel.df()
Show code cell output
✓ added 2 records with ULabel.name for "perturbation": 'IFNG', 'DMSO'
/tmp/ipykernel_3738/4115195754.py:2: DeprecationWarning: `.add_new_from_columns()` is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. It's run by default during initialization.
curator.add_new_from_columns()
| uid | name | description | reference | reference_type | run_id | created_at | created_by_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | ||||||||
| 4 | kxJPUx0C | DMSO | None | None | None | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:40.638011+00:00 | 1 |
| 3 | eJUfcwYN | IFNG | None | None | None | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:40.637911+00:00 | 1 |
| 2 | pava0bEI | perturbation | None | None | None | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:40.620085+00:00 | 1 |
| 1 | lBE1zTbV | Candidate marker study | None | None | None | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:39.049410+00:00 | 1 |
With the ULabel and Feature registries now containing meaningful reference values, validation passes & and we can automatically parse features & labels to save an annotated & curated artifact.
# given the updated registries, the validation passes
curator.validate()
# save curated artifact
artifact = curator.save_artifact(description="my RNA-seq")
# see the parsed annotations
artifact.describe()
# query for a ulabel that was parsed from the dataset
ln.Artifact.get(ulabels__name="IFNG")
Show code cell output
✓ "perturbation" is validated against ULabel.name
→ returning existing artifact with same hash: Artifact(uid='x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001', is_latest=True, description='my RNA-seq', suffix='.parquet', type='dataset', size=3638, hash='PE7xGyIgaqxqJ56hf5ZzVQ', _hash_type='md5', _accessor='DataFrame', visibility=1, _key_is_virtual=True, storage_id=1, transform_id=1, run_id=1, created_by_id=1, created_at=2024-12-21 08:21:39 UTC)
! 3 unique terms (75.00%) are not validated for name: 'CD8A', 'CD4', 'CD14'
! did not create Feature records for 3 non-validated names: 'CD14', 'CD4', 'CD8A'
Artifact .parquet/DataFrame ├── General │ ├── .uid = 'x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001' │ ├── .size = 3638 │ ├── .hash = 'PE7xGyIgaqxqJ56hf5ZzVQ' │ ├── .path = /home/runner/work/lamin-docs/lamin-docs/docs/lamin-intro/.lamindb/x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001.parquet │ ├── .created_by = anonymous │ ├── .created_at = 2024-12-21 08:21:39 │ └── .transform = 'Introduction' ├── Dataset features/.feature_sets │ └── columns • 1 [Feature] │ perturbation cat[ULabel] DMSO, IFNG ├── Linked features │ └── study cat[ULabel] Candidate marker study │ temperature float 21.6 └── Labels └── .cell_types bionty.CellType effector T cell .ulabels ULabel Candidate marker study, IFNG, DMSO
Artifact(uid='x4GHQn89scew7XQt0001', is_latest=True, description='my RNA-seq', suffix='.parquet', type='dataset', size=3638, hash='PE7xGyIgaqxqJ56hf5ZzVQ', _hash_type='md5', _accessor='DataFrame', visibility=1, _key_is_virtual=True, storage_id=1, transform_id=1, run_id=1, created_by_id=1, created_at=2024-12-21 08:21:39 UTC)
Had we used ln.Cuartor from the beginning, we would have caught the typo.
# construct a Curator object to validate & annotate a DataFrame
curator = ln.Curator.from_df(
df_typo,
columns=ln.Feature.name,
categoricals={"perturbation": ln.ULabel.name},
)
# validate the dataset
curator.validate()
Show code cell output
• mapping "perturbation" on ULabel.name
! 1 term is not validated: 'IFNJ'
→ fix typos, remove non-existent values, or save terms via .add_new_from("perturbation")
False
Manage biological registries¶
The generic Feature and ULabel registries will get you pretty far.
But let’s now look at what you do can with a dedicated biological registry like Gene.
Every bionty registry is based on configurable public ontologies (>20 of them).
cell_types = bt.CellType.public()
cell_types
Show code cell output
PublicOntology
Entity: CellType
Organism: all
Source: cl, 2024-05-15
#terms: 2931
cell_types.search("gamma delta T cell").head(2)
Show code cell output
| name | definition | synonyms | parents | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ontology_id |
Validate & annotate with typed features.
import anndata as ad
# store the dataset as an AnnData object to distinguish data from metadata
adata = ad.AnnData(
df[["CD8A", "CD4", "CD14"]], obs=df[["perturbation"]]
)
# create an annotation flow for an AnnData object
curate = ln.Curator.from_anndata(
adata,
# define validation criteria
var_index=bt.Gene.symbol, # map .var.index onto Gene registry
categoricals={adata.obs.perturbation.name: ln.ULabel.name},
organism="human", # specify the organism for the Gene registry
)
curate.validate()
# save curated artifact
artifact = curate.save_artifact(description="my RNA-seq")
artifact.describe()
Show code cell output
! indexing datasets with gene symbols can be problematic: https://docs.lamin.ai/faq/symbol-mapping
• saving validated records of 'var_index'
✓ added 3 records from public with Gene.symbol for "var_index": 'CD8A', 'CD4', 'CD14'
✓ "var_index" is validated against Gene.symbol
✓ "perturbation" is validated against ULabel.name
Artifact .h5ad/AnnData ├── General │ ├── .uid = '5tMDIC7WsSsZ1s2m0000' │ ├── .size = 19240 │ ├── .hash = 'nLH34gqty3-5c2eGF6deOA' │ ├── .n_observations = 3 │ ├── .path = /home/runner/work/lamin-docs/lamin-docs/docs/lamin-intro/.lamindb/5tMDIC7WsSsZ1s2m0000.h5ad │ ├── .created_by = anonymous │ ├── .created_at = 2024-12-21 08:21:43 │ └── .transform = 'Introduction' ├── Dataset features/.feature_sets │ ├── obs • 1 [Feature] │ │ perturbation cat[ULabel] DMSO, IFNG │ └── var • 3 [bionty.Gene] │ CD8A int │ CD4 int │ CD14 int └── Labels └── .ulabels ULabel IFNG, DMSO
Query for typed features.
# get a lookup object for human genes
genes = bt.Gene.filter(organism__name="human").lookup()
# query for all feature sets that contain CD8A
feature_sets = ln.FeatureSet.filter(genes=genes.cd8a).all()
# write the query
ln.Artifact.filter(feature_sets__in=feature_sets).df()
Show code cell output
| uid | key | description | suffix | type | size | hash | n_objects | n_observations | _hash_type | _accessor | visibility | _key_is_virtual | storage_id | transform_id | version | is_latest | run_id | created_at | created_by_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 5tMDIC7WsSsZ1s2m0000 | None | my RNA-seq | .h5ad | dataset | 19240 | nLH34gqty3-5c2eGF6deOA | None | 3 | md5 | AnnData | 1 | True | 1 | 1 | None | True | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:43.292886+00:00 | 1 |
Update ontologies, e.g., create a cell type record and add a new cell state.
# create an ontology-coupled cell type record and save it
neuron = bt.CellType.from_source(name="neuron").save()
# create a record to track a new cell state
new_cell_state = bt.CellType(name="my neuron cell state", description="explains X").save()
# express that it's a neuron state
new_cell_state.parents.add(neuron)
# view ontological hierarchy
new_cell_state.view_parents(distance=2)
Show code cell output
✓ created 1 CellType record from Bionty matching name: 'neuron'
✓ created 3 CellType records from Bionty matching ontology_id: 'CL:0000393', 'CL:0000404', 'CL:0002319'
Scale learning¶
How do you integrate new datasets with your existing datasets? Leverage Collection.
# a new dataset
df = pd.DataFrame(
{"CD8A": [2, 3, 3], "CD4": [3, 4, 5], "CD38": [4, 2, 3], "perturbation": ["DMSO", "IFNG", "IFNG"],},
index=["sample4", "sample5", "sample6"],
)
adata = ad.AnnData(df[["CD8A", "CD4", "CD38"]], obs=df[["perturbation"]])
# validate, curate and save a new artifact
curate = ln.Curator.from_anndata(
adata,
var_index=bt.Gene.symbol,
categoricals={adata.obs.perturbation.name: ln.ULabel.name},
organism="human",
)
curate.validate()
artifact2 = curate.save_artifact(description="my RNA-seq dataset 2")
Show code cell output
! indexing datasets with gene symbols can be problematic: https://docs.lamin.ai/faq/symbol-mapping
• saving validated records of 'var_index'
✓ added 1 record from public with Gene.symbol for "var_index": 'CD38'
✓ "var_index" is validated against Gene.symbol
✓ "perturbation" is validated against ULabel.name
Create a collection using Collection.
collection = ln.Collection([artifact, artifact2], name="my RNA-seq collection").save()
collection.describe()
collection.view_lineage()
Show code cell output
Collection └── General ├── .uid = '1El6wgurgchzzflF0000' ├── .hash = 'xDjhklRxArFHharWMZPEzw' ├── .created_by = anonymous ├── .created_at = 2024-12-21 08:21:45 └── .transform = 'Introduction'
# if it's small enough, you can load the entire collection into memory as if it was one
collection.load()
# typically, it's too big, hence, iterate over its artifacts
collection.artifacts.all()
# or look at a DataFrame listing the artifacts
collection.artifacts.df()
Show code cell output
| uid | key | description | suffix | type | size | hash | n_objects | n_observations | _hash_type | _accessor | visibility | _key_is_virtual | storage_id | transform_id | version | is_latest | run_id | created_at | created_by_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 5tMDIC7WsSsZ1s2m0000 | None | my RNA-seq | .h5ad | dataset | 19240 | nLH34gqty3-5c2eGF6deOA | None | 3 | md5 | AnnData | 1 | True | 1 | 1 | None | True | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:43.292886+00:00 | 1 |
| 4 | 7ROKR84LAp41aeyZ0000 | None | my RNA-seq dataset 2 | .h5ad | dataset | 19240 | K95PcyOoxIxtlytXMr6AVg | None | 3 | md5 | AnnData | 1 | True | 1 | 1 | None | True | 1 | 2024-12-21 08:21:45.867530+00:00 | 1 |
Directly train models on collections of AnnData.
# to train models, batch iterate through the collection as if it was one array
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, WeightedRandomSampler
dataset = collection.mapped(obs_keys=["perturbation"])
sampler = WeightedRandomSampler(
weights=dataset.get_label_weights("perturbation"), num_samples=len(dataset)
)
data_loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=2, sampler=sampler)
for batch in data_loader:
pass
Read this blog post for more on training models on sharded datasets.
Design¶
World model¶
Teams need to have enough freedom to initiate work independently but enough structure to easily integrate datasets later on
Batched datasets (
Artifact) from physical instruments are transformed (Transform) into useful representationsLearning needs features (
Feature,CellMarker, …) and labels (ULabel,CellLine, …)Insights connect dataset representations with experimental metadata and knowledge (ontologies)
Architecture¶
LaminDB is a distributed system like git that can be run or hosted anywhere. As infrastructure, you merely need a database (SQLite/Postgres) and a storage location (file system, S3, GCP, HuggingFace, …).
You can easily create your new local instance:
lamin init --storage ./my-data-folder
import lamindb as ln
ln.setup.init(storage="./my-data-folder")
Or you can let collaborators connect to a cloud-hosted instance:
lamin connect account-handle/instance-name
import lamindb as ln
ln.connect("account-handle/instance-name")
library(laminr)
ln <- connect("account-handle/instance-name")
For learning more about how to create & host LaminDB instances on distributed infrastructure, see Install & setup. LaminDB instances work standalone but can optionally be managed by LaminHub. For an architecture diagram of LaminHub, reach out!
Metada schema & API¶
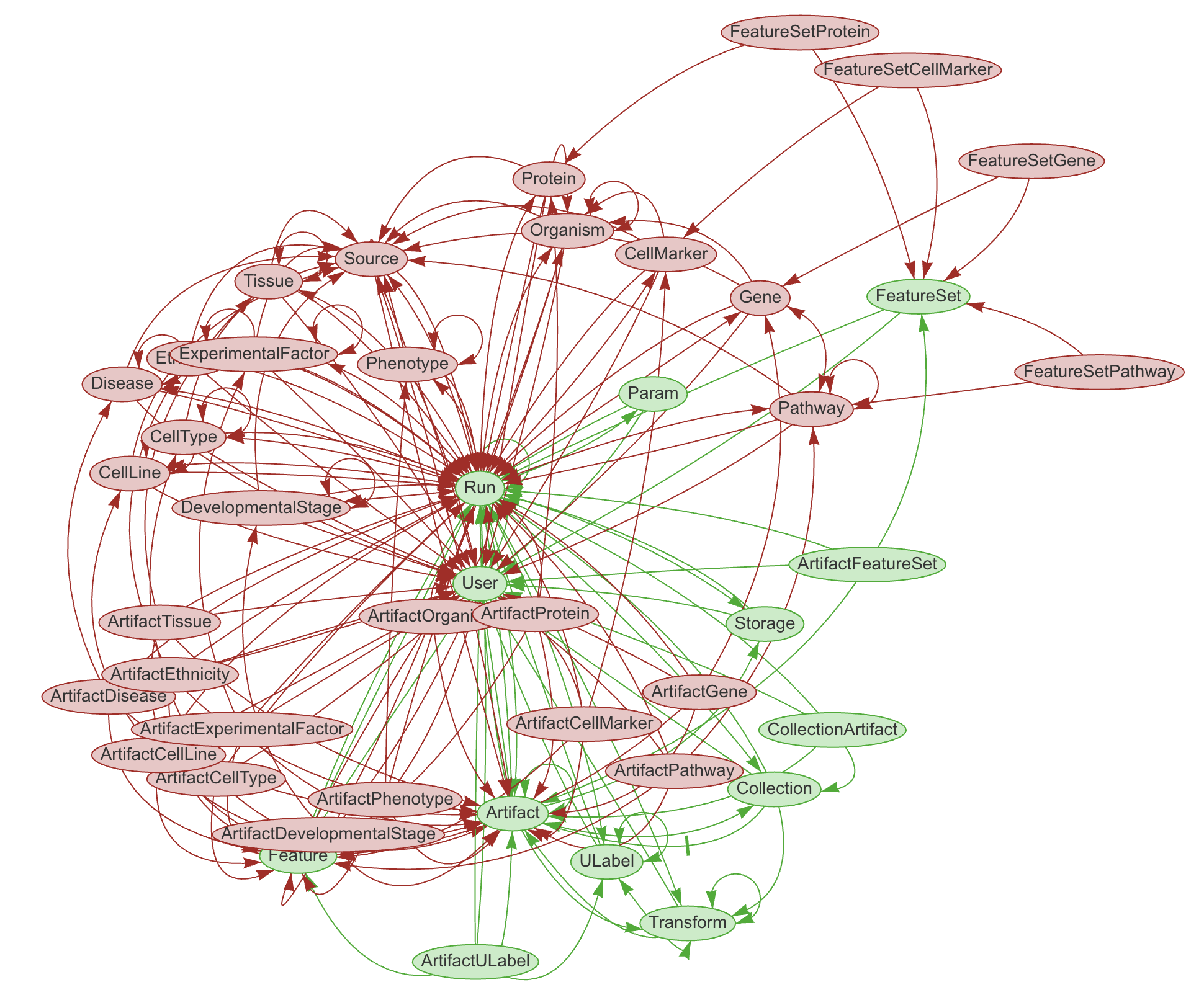
LaminDB provides a SQL schema for common metadata entities: Artifact, Collection, Transform, Feature, ULabel etc. - see the API reference or the source code.
The core metadata schema is extendable through plugins (see green vs. red entities in graphic), e.g., with basic biological (Gene, Protein, CellLine, etc.) & operational entities (Biosample, Techsample, Treatment, etc.).
What is the metadata schema language?
Data models are defined in Python using the Django ORM. Django translates them to SQL tables. Django is one of the most-used & highly-starred projects on GitHub (~1M dependents, ~73k stars) and has been robustly maintained for 15 years.
On top of the metadata schema, LaminDB is a Python API that models datasets as artifacts, abstracts over storage & database access, data transformations, and (biological) ontologies.
Note that the datasets schema (e.g., .parquet files or .h5ad arrays) is modeled through the Feature registry and does not require migrations to be updated.
Custom schemas and plugins¶
LaminDB can be customized & extended with schema & app plugins building on the Django ecosystem. Examples are:
bionty: Registries for basic biological entities, coupled to public ontologies.
wetlab: Registries for samples, treatments, etc.
If you’d like to create your own schema or app:
Create a git repository with registries similar to wetlab
Create & deploy migrations via
lamin migrate createandlamin migrate deploy
Repositories¶
LaminDB and its plugins consist in open-source Python libraries & publicly hosted metadata assets:
lamindb: Core package.
bionty: Registries for basic biological entities, coupled to public ontologies.
wetlab: Registries for samples, treatments, etc.
usecases: Use cases as visible on the docs.
All immediate dependencies are available as git submodules here, for instance,
lnschema-core: Core schema.
lamindb-setup: Setup & configure LaminDB.
lamin-cli: CLI for
lamindbandlamindb-setup.
For a comprehensive list of open-sourced software, browse our GitHub account.
lamin-utils: Generic utilities, e.g., a logger.
readfcs: FCS artifact reader.
nbproject: Light-weight Jupyter notebook tracker.
bionty-assets: Assets for public biological ontologies.
LaminHub is not open-sourced.
Influences¶
LaminDB was influenced by many other projects, see Influences.

