lamindb.Artifact  ¶
¶
- class lamindb.Artifact(path: UPathStr, *, key: str | None = None, description: str | None = None, kind: ArtifactKind | str | None = None, features: dict[str, Any] | None = None, schema: Schema | None = None, revises: Artifact | None = None, overwrite_versions: bool | None = None, run: Run | False | None = None, storage: Storage | None = None, branch: Branch | None = None, space: Space | None = None, skip_hash_lookup: bool = False)¶
Bases:
SQLRecord,IsVersioned,TracksRun,TracksUpdatesDatasets & models stored as files, folders, or arrays.
Some artifacts are table- or array-like, e.g., when stored as
.parquet,.h5ad,.zarr, or.tiledb.- Parameters:
path –
UPathStrA path to a local or remote folder or file from which to create the artifact.key –
str | None = NoneA key within the storage location, e.g.,"myfolder/myfile.fcs". Artifacts with the same key form a version family.description –
str | None = NoneA description.kind –
Literal["dataset", "model"] | str | None = NoneDistinguish models from datasets from other files & folders.features –
dict | None = NoneExternal features to annotate the artifact with viaset_values.schema –
Schema | None = NoneA schema to validate features.revises –
Artifact | None = NonePrevious version of the artifact. An alternative to passingkeywhen creating a new version.overwrite_versions –
bool | None = NoneWhether to overwrite versions. Defaults toTruefor folders andFalsefor files.run –
Run | bool | None = NoneThe run that creates the artifact. IfFalse, suppress tracking the run. IfNone, infer the run from the global run context.branch –
Branch | None = NoneThe branch of the artifact. IfNone, uses the current branch.space –
Space | None = NoneThe space of the artifact. IfNone, uses the current space.storage –
Storage | None = NoneThe storage location for the artifact. IfNone, uses the default storage location. You can see and set the default storage location instorage.skip_hash_lookup –
bool = FalseSkip the hash lookup so that a new artifact is created even if an artifact with the same hash already exists.
Examples
Create an artifact from a local file or folder:
artifact = ln.Artifact("./my_file.parquet", key="examples/my_file.parquet").save() artifact = ln.Artifact("./my_folder", key="project1/my_folder").save()
Calling
.save()copies or uploads the file to the default storage location of your lamindb instance. If you create an artifact from a remote file or folder, lamindb registers the S3keyand avoids copying the data:artifact = ln.Artifact("s3://my_bucket/my_folder/my_file.csv").save()
If you then want to query & access the artifact later on, this is how you do it:
artifact = ln.Artifact.get(key="examples/my_file.parquet") cached_path = artifact.cache() # sync to local cache & get local path
If the storage format supports it, you can load the artifact directly into memory or query it through a streaming interface, e.g., for parquet files:
df = artifact.load() # load parquet file as DataFrame pyarrow_dataset = artifact.open() # open a streaming file-like object
If you want to validate & annotate a dataframe or an array using the feature & label registries, pass
schemato one of the.from_dataframe(),.from_anndata(), … constructors:artifact = ln.Artifact.from_dataframe( "./my_file.parquet", key="my_dataset.parquet", schema="valid_features" ).save()
To annotate by external features:
artifact = ln.Artifact("./my_file.parquet", features={"cell_type_by_model": "T cell"}).save()
You can make a new version of an artifact by passing an existing
key:artifact_v2 = ln.Artifact("./my_file.parquet", key="examples/my_file.parquet").save() artifact_v2.versions.to_dataframe() # see all versions
You can write artifacts to non-default storage locations by passing the
storageargument:storage_loc = ln.Storage.get(root="s3://my_bucket") # get storage location, or create via ln.Storage(root="s3://my_bucket").save() ln.Artifact("./my_file.parquet", key="examples/my_file.parquet", storage=storage_loc).save() # upload to s3://my_bucket
Sometimes you want to avoid mapping the artifact into a path hierarchy, and you only pass
description:artifact = ln.Artifact("./my_folder", description="My folder").save() artifact_v2 = ln.Artifact("./my_folder", revises=old_artifact).save() # need to version based on `revises`, a shared description does not trigger a new version
Notes
Storage formats & object types
The
Artifactregistry tracks the storage format viasuffixand an abstract object type viaotype.description
Python type examples
table
.csv,.tsv,.parquet,.ipc"DataFrame"pandas.DataFrame,polars.DataFrame,pyarrow.Tableannotated matrix
.h5ad,.zarr,.h5mu"AnnData"anndata.AnnDatastacked matrix
.zarr.tiledbsoma"MuData""tiledbsoma"mudata.MuDatatiledbsoma.Experimentspatial data
.zarr"SpatialData"spatialdata.SpatialDatageneric arrays
.h5,.zarr,.tiledb—
h5py.Dataset,zarr.Array,tiledb.Arrayunstructured
.fastq,.pdf,.vcf,.html—
—
You can map storage formats onto R types, e.g., an
AnnDatamight be accessed viaanndataR.Because
otypeaccepts anystr, you can define custom object types that enable queries & logic that you need, e.g.,"SingleCellExperiment"or"MyCustomZarrDataStructure".LaminDB makes some default choices (e.g., serialize a
DataFrameas a.parquetfile).Will artifacts get duplicated?
If an artifact with the exact same hash already exists,
Artifact()returns the existing artifact.In concurrent workloads where the same artifact is created repeatedly at the exact same time,
.save()detects the duplication and will return the existing artifact.Why does the constructor look the way it looks?
It’s inspired by APIs building on AWS S3.
Both boto3 and quilt select a bucket (a storage location in LaminDB) and define a target path through a
keyargument.In boto3:
# signature: S3.Bucket.upload_file(filepath, key) import boto3 s3 = boto3.resource('s3') bucket = s3.Bucket('mybucket') bucket.upload_file('/tmp/hello.txt', 'hello.txt')
In quilt3:
# signature: quilt3.Bucket.put_file(key, filepath) import quilt3 bucket = quilt3.Bucket('mybucket') bucket.put_file('hello.txt', '/tmp/hello.txt')
See also
StorageStorage locations for artifacts.
CollectionCollections of artifacts.
from_dataframe()Create an artifact from a
DataFrame.from_anndata()Create an artifact from an
AnnData.
Attributes¶
- property features: FeatureManager¶
Feature manager.
Typically, you annotate a dataset with features by defining a
Schemaand passing it to theArtifactconstructor.Here is how to do annotate an artifact ad hoc:
artifact.features.add_values({ "species": "human", "scientist": ['Barbara McClintock', 'Edgar Anderson'], "temperature": 27.6, "experiment": "Experiment 1" })
Query artifacts by features:
ln.Artifact.filter(scientist="Barbara McClintock")
Note: Features may or may not be part of the dataset, i.e., the artifact content in storage. For instance, the
DataFrameCuratorflow validates the columns of aDataFrame-like artifact and annotates it with features corresponding to these columns.artifact.features.add_values, by contrast, does not validate the content of the artifact.To get all feature values:
dictionary_of_values = artifact.features.get_values()
The dicationary above uses identifiers, like the string “human” for an
Organismobject. The below, by contrast, returns a Python object for categorical features:organism = artifact.features["species"] # returns an Organism object, not "human" temperature = artifact.features["temperature"] # returns a temperature value, a float
You can also validate external feature annotations with a
schema:schema = ln.Schema([ln.Feature(name="species", dtype=str).save()]).save() artifact.features.add_values({"species": "bird"}, schema=schema)
- property labels: LabelManager¶
Label manager.
A way to access all label annotations of an artifact, irrespective of their type.
To annotate with labels, use the type-specific accessor, for example:
experiment = ln.Record(name="Experiment 1").save() artifact.records.add(experiment) project = ln.Project(name="Project A").save() artifact.projects.add(project)
- property overwrite_versions: bool¶
Indicates whether to keep or overwrite versions.
It defaults to
Falsefor file-like artifacts and toTruefor folder-like artifacts.Note that this requires significant storage space for large folders with many duplicated files. Currently,
lamindbdoes not de-duplicate files across versions as in git, but keeps all files for all versions of the folder in storage.
- property path: Path¶
Path.
Example:
import lamindb as ln # File in cloud storage, here AWS S3: artifact = ln.Artifact("s3://my-bucket/my-file.csv").save() artifact.path #S3QueryPath('s3://my-bucket/my-file.csv') # File in local storage: ln.Artifact("./myfile.csv", key="myfile.csv").save() artifact.path #> PosixPath('/home/runner/work/lamindb/lamindb/docs/guide/mydata/myfile.csv')
- property stem_uid: str¶
Universal id characterizing the version family.
The full uid of a record is obtained via concatenating the stem uid and version information:
stem_uid = random_base62(n_char) # a random base62 sequence of length 12 (transform) or 16 (artifact, collection) version_uid = "0000" # an auto-incrementing 4-digit base62 number uid = f"{stem_uid}{version_uid}" # concatenate the stem_uid & version_uid
- property version: str¶
The version of an object.
Defines version of an object within a family of objects characterized by the same
stem_uid.Returns
.version_tagif set, otherwise the last 4 characters of theuid.
Simple fields¶
- uid: str¶
A universal random id.
- key: str | None¶
A (virtual) relative file path within the artifact’s storage location.
Setting a
keyis useful to automatically group artifacts into a version family.LaminDB defaults to a virtual file path to make renaming of data in object storage easy.
If you register existing files in a storage location, the
keyequals the actual filepath on the underyling filesytem or object store.
- description: str | None¶
A description.
- suffix: str¶
The path suffix or an empty string if no suffix exists.
This is either a file suffix (
".csv",".h5ad", etc.) or the empty string “”.
- kind: ArtifactKind | str | None¶
ArtifactKindor customstrvalue (defaultNone).
- otype: Literal['DataFrame', 'AnnData', 'MuData', 'SpatialData', 'tiledbsoma'] | str | None¶
The object type represented as a string.
The field is automatically set when using the
from_dataframe(),from_anndata(), … constructors. Unstructured artifacts haveotype=None.The field also accepts custom
strvalues to allow for building logic around them in third-party packages.See section storage formats & object types for more background.
- size: int | None¶
The size in bytes.
Examples: 1KB is 1e3 bytes, 1MB is 1e6, 1GB is 1e9, 1TB is 1e12 etc.
- hash: str | None¶
The hash or pseudo-hash of the artifact content in storage.
Useful to ascertain integrity and avoid duplication.
Different versions of the artifact have different hashes.
- n_files: int | None¶
The number of files for folder-like artifacts.
Is
Nonefor file-like artifacts.Note that some arrays are also stored as folders, e.g.,
.zarror.tiledbsoma.
- n_observations: int | None¶
The number of observations in this artifact.
Typically, this denotes the first array dimension.
- version_tag: str | None¶
Version tag (default
None).Consider using semantic versioning with Python versioning.
- is_latest: bool¶
Boolean flag that indicates whether a record is the latest in its version family.
- is_locked: bool¶
Whether the object is locked for edits.
- created_at: datetime¶
Time of creation of record.
- updated_at: datetime¶
Time of last update to record.
Relational fields¶
- created_on¶
- run: Run¶
The run that created the artifact ←
output_artifacts.
- schema: Schema | None¶
The validating schema of this artifact ←
validated_artifacts.The validating schema is helpful to query artifacts that were validated by the same schema.
- created_by: User¶
The creator of this artifact ←
created_artifacts.
- input_of_runs: RelatedManager[Run]¶
The runs that use this artifact as an input ←
input_artifacts.
- recreating_runs: RelatedManager[Run]¶
The runs that re-created the artifact after its initial creation ←
recreated_artifacts.
- schemas: RelatedManager[Schema]¶
The inferred schemas of this artifact ←
artifacts.The inferred schemas are helpful to answer the question: “Which features are present in the artifact?”
The validating schema typically allows a range of valid actual dataset schemas. The inferred schemas link the actual schemas of the artifact, and are auto-generated by parsing the artifact content during validation.
- json_values: RelatedManager[JsonValue]¶
The feature-indexed JSON values annotating this artifact ←
artifacts.
- artifacts: RelatedManager[Artifact]¶
The annotating artifacts of this artifact ←
linked_by_artifacts.
- linked_in_records: RelatedManager[Record]¶
The records linking this artifact as a feature value ←
linked_artifacts.
- users: RelatedManager[User]¶
The users annotating this artifact ←
artifacts.
- runs: RelatedManager[Run]¶
The runs annotating this artifact ←
artifacts.
- linked_by_runs: RelatedManager[Run]¶
The runs linking this artifact ←
linked_by_artifacts.
- ulabels: RelatedManager[ULabel]¶
The ulabels annotating this artifact ←
artifacts.
- linked_by_artifacts: RelatedManager[Artifact]¶
The artifacts annotated by this artifact ←
artifacts.
- collections: RelatedManager[Collection]¶
The collections that this artifact is part of ←
artifacts.
- records: RelatedManager[Record]¶
The records annotating this artifact ←
artifacts.
- references: RelatedManager[Reference]¶
The references annotating this artifact ←
artifacts.
- projects: RelatedManager[Project]¶
The projects annotating this artifact ←
artifacts.
- ablocks: RelatedManager[ArtifactBlock]¶
Attached blocks ←
artifact.
Class methods¶
- get(*, key=None, path=None, is_run_input=False, **expressions)¶
Get a single record.
- Parameters:
idlike (int | str | None, default:
None) – Either a uid stub, uid or an integer id.expressions – Fields and values passed as Django query expressions.
- Raises:
lamindb.errors.ObjectDoesNotExist – In case no matching record is found.
- Return type:
Artifact
See also
Guide: Query & search registries
Django documentation: Queries
Examples
record = ln.Record.get("FvtpPJLJ") record = ln.Record.get(name="my-label")
- filter(**expressions)¶
Query records.
- Parameters:
queries – One or multiple
Qobjects.expressions – Fields and values passed as Django query expressions.
- Return type:
See also
Guide: Query & search registries
Django documentation: Queries
Examples
>>> ln.Project(name="my label").save() >>> ln.Project.filter(name__startswith="my").to_dataframe()
- classmethod from_lazy(suffix, overwrite_versions, key=None, description=None, run=None, **kwargs)¶
Create a lazy artifact for streaming to auto-generated internal paths.
This is needed when it is desirable to stream to a
lamindbauto-generated internal path and register the path as an artifact. It allows writing directly into the default cloud (or local) storage of the current instance and then saving as anArtifact.The lazy artifact object (see
LazyArtifact) creates a real artifact on.save()with the provided arguments.- Parameters:
suffix (
str) – The suffix for the auto-generated internal pathoverwrite_versions (
bool) – Whether to overwrite versions.key (
str|None, default:None) – An optional key to reference the artifact.description (
str|None, default:None) – A description.run (
Run|None, default:None) – The run that creates the artifact.**kwargs – Other keyword arguments for the artifact to be created.
- Return type:
Examples
Local storage: create a lazy artifact, stream to the path, then save:
lazy = ln.Artifact.from_lazy(suffix=".zarr", overwrite_versions=True, key="mydata.zarr") zarr.open(lazy.path, mode="w")["test"] = np.array(["test"]) artifact = lazy.save()
Cloud storage (e.g. S3): use
zarr.storage.FsspecStoreto stream arrays:lazy = ln.Artifact.from_lazy(suffix=".zarr", overwrite_versions=True, key="mydata.zarr") store = zarr.storage.FsspecStore.from_url(lazy.path.as_posix()) group = zarr.open(store, mode="w") group["ones"] = np.ones(3) artifact = lazy.save()
- classmethod from_dataframe(df, *, key=None, description=None, run=None, revises=None, schema=None, features=None, parquet_kwargs=None, csv_kwargs=None, **kwargs)¶
Create from
DataFrame, optionally validate & annotate.Sets
.otypeto"DataFrame"and populates.n_observations.- Parameters:
df (pd.DataFrame | UPathStr) – A
DataFrameobject or aUPathStrpointing to aDataFramein storage, e.g. a.parquetor.csvfile.key (str | None, default:
None) – A relative path within default storage, e.g.,"myfolder/myfile.parquet".description (str | None, default:
None) – A description.revises (Artifact | None, default:
None) – An old version of the artifact.run (Run | None, default:
None) – The run that creates the artifact.schema (Schema | Literal[‘valid_features’] | None, default:
None) – A schema that defines how to validate & annotate.features (dict[str, Any] | None, default:
None) – Additional external features to annotate the artifact viaset_values.parquet_kwargs (dict[str, Any] | None, default:
None) – Additional keyword arguments passed to thepandas.DataFrame.to_parquetmethod, which are passed on topyarrow.parquet.ParquetWriter.csv_kwargs (dict[str, Any] | None, default:
None) – Additional keyword arguments passed to thepandas.DataFrame.to_csvmethod.
- Return type:
Artifact
Examples
No validation and annotation:
ln.Artifact.from_dataframe(df, key="examples/dataset1.parquet").save()
With validation and annotation:
ln.Artifact.from_dataframe(df, key="examples/dataset1.parquet", schema="valid_features").save()
Under-the-hood, this uses the following build-in schema (
valid_features()):schema = ln.Schema(name="valid_features", itype="Feature").save()
External features:
import lamindb as ln from datetime import date df = ln.examples.datasets.mini_immuno.get_dataset1(otype="DataFrame") temperature = ln.Feature(name="temperature", dtype=float).save() date_of_study = ln.Feature(name="date_of_study", dtype=date).save() external_schema = ln.Schema(features=[temperature, date_of_study]).save() concentration = ln.Feature(name="concentration", dtype=str).save() donor = ln.Feature(name="donor", dtype=str, nullable=True).save() schema = ln.Schema( features=[concentration, donor], slots={"__external__": external_schema}, otype="DataFrame", ).save() artifact = ln.Artifact.from_dataframe( df, key="examples/dataset1.parquet", features={"temperature": 21.6, "date_of_study": date(2024, 10, 1)}, schema=schema, ).save() artifact.describe()
Parquet kwargs:
import lamindb as ln import pandas as pd import pyarrow.parquet as pq def test_parquet_kwargs(): df = pd.DataFrame( { "a": [3, 1, 4, 2], "b": ["c", "a", "d", "b"], "c": [3.3, 1.1, 4.4, 2.2], } ) df_sorted = df.sort_values(by=["a", "b"]) sorting_columns = [ pq.SortingColumn(0, descending=False, nulls_first=False), pq.SortingColumn(1, descending=False, nulls_first=False), ] artifact = ln.Artifact.from_dataframe( df_sorted, key="df_sorted.parquet", parquet_kwargs={"sorting_columns": sorting_columns}, ).save() pyarrow_dataset = artifact.open() fragment = next(pyarrow_dataset.get_fragments()) assert list(fragment.metadata.row_group(0).sorting_columns) == sorting_columns
- classmethod from_anndata(adata, *, key=None, description=None, run=None, revises=None, schema=None, **kwargs)¶
Create from
AnnData, optionally validate & annotate.Sets
.otypeto"AnnData"and populates.n_observations.- Parameters:
adata (
AnnData| lamindb.core.types.UPathStr) – AnAnnDataobject or a path of AnnData-like.key (
str|None, default:None) – A relative path within default storage, e.g.,"myfolder/myfile.h5ad".description (
str|None, default:None) – A description.revises (
Artifact|None, default:None) – An old version of the artifact.run (
Run|None, default:None) – The run that creates the artifact.schema (
Schema|Literal['ensembl_gene_ids_and_valid_features_in_obs'] |None, default:None) – A schema that defines how to validate & annotate.
- Return type:
See also
Collection()Track collections.
FeatureTrack features.
Example
No validation and annotation:
ln.Artifact.from_anndata(adata, key="examples/dataset1.h5ad").save()
With validation and annotation:
ln.Artifact.from_anndata(adata, key="examples/dataset1.h5ad", schema="ensembl_gene_ids_and_valid_features_in_obs").save()
Under-the-hood, this uses the following build-in schema (
anndata_ensembl_gene_ids_and_valid_features_in_obs()):import bionty as bt import lamindb as ln obs_schema = ln.examples.schemas.valid_features() varT_schema = ln.Schema( name="valid_ensembl_gene_ids", itype=bt.Gene.ensembl_gene_id ).save() schema = ln.Schema( name="anndata_ensembl_gene_ids_and_valid_features_in_obs", otype="AnnData", slots={"obs": obs_schema, "var.T": varT_schema}, ).save()
This schema tranposes the
varDataFrame during curation, so that one validates and annotates the columns ofvar.T, i.e.,[ENSG00000153563, ENSG00000010610, ENSG00000170458]. If one doesn’t transpose, one would annotate the columns ofvar, i.e.,[gene_symbol, gene_type].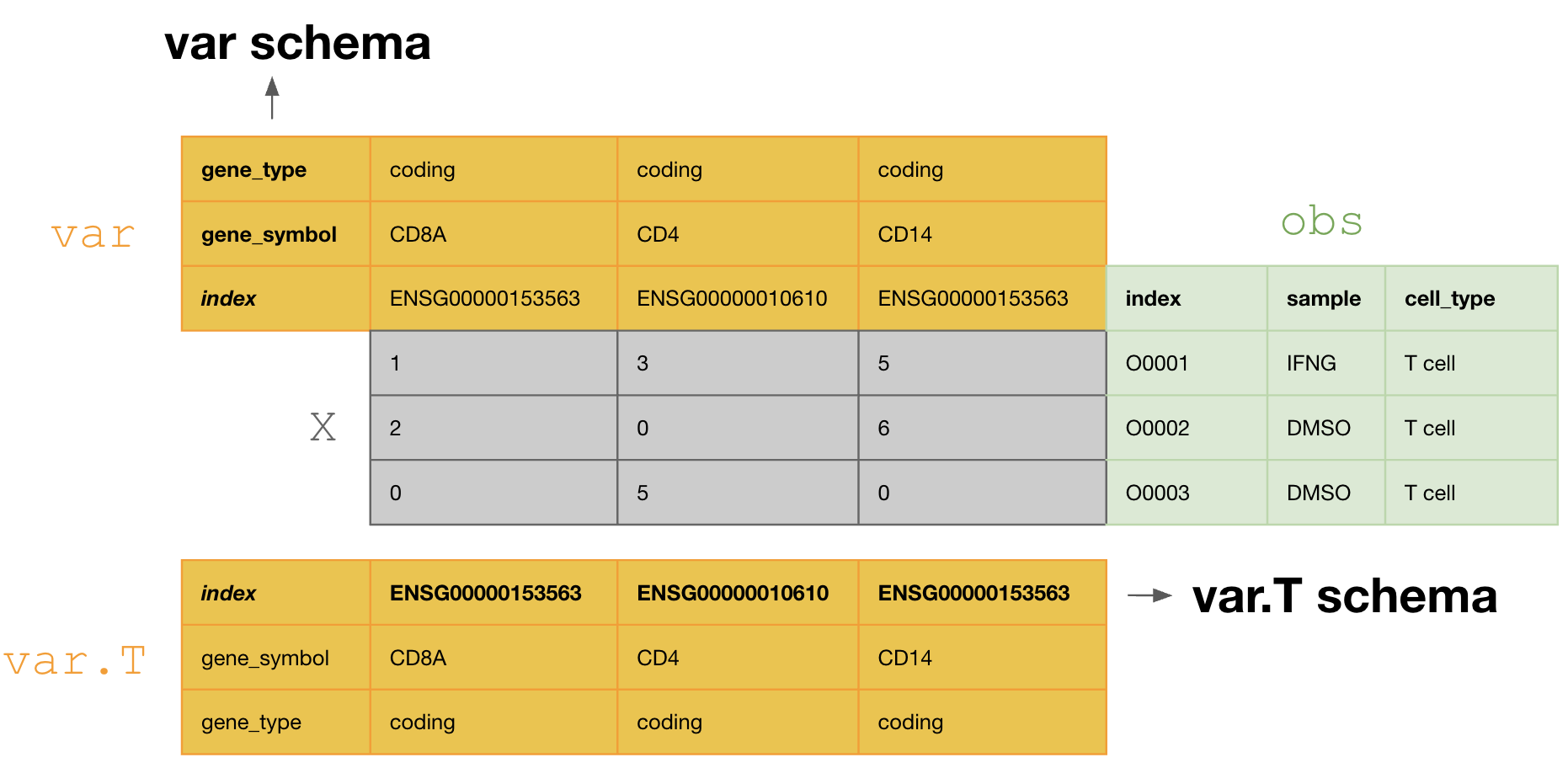
- classmethod from_mudata(mdata, *, key=None, description=None, run=None, revises=None, schema=None, **kwargs)¶
Create from
MuData, optionally validate & annotate.Sets
.otypeto"MuData".- Parameters:
mdata (
MuData| lamindb.core.types.UPathStr) – AMuDataobject.key (
str|None, default:None) – A relative path within default storage, e.g.,"myfolder/myfile.h5mu".description (
str|None, default:None) – A description.revises (
Artifact|None, default:None) – An old version of the artifact.run (
Run|None, default:None) – The run that creates the artifact.schema (
Schema|None, default:None) – A schema that defines how to validate & annotate.
- Return type:
See also
Collection()Track collections.
FeatureTrack features.
Example:
import lamindb as ln mdata = ln.examples.datasets.mudata_papalexi21_subset() artifact = ln.Artifact.from_mudata(mdata, key="mudata_papalexi21_subset.h5mu").save()
- classmethod from_spatialdata(sdata, *, key=None, description=None, run=None, revises=None, schema=None, **kwargs)¶
Create from
SpatialData, optionally validate & annotate.Sets
.otypeto"SpatialData".- Parameters:
sdata (SpatialData | UPathStr) – A
SpatialDataobject.key (str | None, default:
None) – A relative path within default storage, e.g.,"myfolder/myfile.zarr".description (str | None, default:
None) – A description.revises (Artifact | None, default:
None) – An old version of the artifact.run (Run | None, default:
None) – The run that creates the artifact.schema (Schema | None, default:
None) – A schema that defines how to validate & annotate.
- Return type:
Artifact
See also
Collection()Track collections.
FeatureTrack features.
Example
No validation and annotation:
import lamindb as ln artifact = ln.Artifact.from_spatialdata(sdata, key="my_dataset.zarr").save()
With validation and annotation.
import lamindb as ln import bionty as bt attrs_schema = ln.Schema( features=[ ln.Feature(name="bio", dtype=dict).save(), ln.Feature(name="tech", dtype=dict).save(), ], ).save() sample_schema = ln.Schema( features=[ ln.Feature(name="disease", dtype=bt.Disease, coerce=True).save(), ln.Feature( name="developmental_stage", dtype=bt.DevelopmentalStage, coerce=True, ).save(), ], ).save() tech_schema = ln.Schema( features=[ ln.Feature(name="assay", dtype=bt.ExperimentalFactor, coerce=True).save(), ], ).save() obs_schema = ln.Schema( features=[ ln.Feature(name="sample_region", dtype="str").save(), ], ).save() uns_schema = ln.Schema( features=[ ln.Feature(name="analysis", dtype="str").save(), ], ).save() # Schema enforces only registered Ensembl Gene IDs are valid (maximal_set=True) varT_schema = ln.Schema(itype=bt.Gene.ensembl_gene_id, maximal_set=True).save() sdata_schema = ln.Schema( name="spatialdata_blobs_schema", otype="SpatialData", slots={ "attrs:bio": sample_schema, "attrs:tech": tech_schema, "attrs": attrs_schema, "tables:table:obs": obs_schema, "tables:table:var.T": varT_schema, }, ).save()
import lamindb as ln spatialdata = ln.examples.datasets.spatialdata_blobs() sdata_schema = ln.Schema.get(name="spatialdata_blobs_schema") curator = ln.curators.SpatialDataCurator(spatialdata, sdata_schema) try: curator.validate() except ln.errors.ValidationError: pass spatialdata.tables["table"].var.drop(index="ENSG00000999999", inplace=True) # validate again (must pass now) and save artifact artifact = ln.Artifact.from_spatialdata( spatialdata, key="examples/spatialdata1.zarr", schema=sdata_schema ).save() artifact.describe()
- classmethod from_tiledbsoma(exp, *, key=None, description=None, run=None, revises=None, **kwargs)¶
Create from a
tiledbsoma.Experimentstore.Sets
.otypeto"tiledbsoma"and populates.n_observations.- Parameters:
exp (SOMAExperiment | UPathStr) – TileDB-SOMA Experiment object or path to Experiment store.
key (str | None, default:
None) – A relative path within default storage, e.g.,"myfolder/mystore.tiledbsoma".description (str | None, default:
None) – A description.revises (Artifact | None, default:
None) – An old version of the artifact.run (Run | None, default:
None) – The run that creates the artifact.
- Return type:
Artifact
Example:
import lamindb as ln artifact = ln.Artifact.from_tiledbsoma("s3://mybucket/store.tiledbsoma", description="a tiledbsoma store").save()
- classmethod from_dir(path, *, key=None, run=None)¶
Create a list of
Artifactobjects from a directory.Hint
If you have a high number of files (several 100k) and don’t want to track them individually, create a single
ArtifactviaArtifact(path)for them. See, e.g., RxRx: cell imaging.- Parameters:
path (lamindb.core.types.UPathStr) – Source path of folder.
key (
str|None, default:None) – Key for storage destination. IfNoneand directory is in a registered location, the inferredkeywill reflect the relative position. IfNoneand directory is outside of a registered storage location, the inferred key defaults topath.name.run (
Run|None, default:None) – ARunobject.
- Return type:
SQLRecordList
Example:
import lamindb as ln dir_path = ln.examples.datasets.dir_scrnaseq_cellranger("sample_001", ln.settings.storage) ln.Artifact.from_dir(dir_path).save() # creates one artifact per file in dir_path
- classmethod to_dataframe(include=None, features=False, limit=100)¶
Evaluate and convert to
pd.DataFrame.By default, maps simple fields and foreign keys onto
DataFramecolumns.Guide: Query & search registries
- Parameters:
include (
str|list[str] |None, default:None) – Related data to include as columns. Takes strings of form"records__name","cell_types__name", etc. or a list of such strings. ForArtifact,Record, andRun, can also pass"features"to include features with data types pointing to entities in the core schema. If"privates", includes private fields (fields starting with_).features (
bool|list[str], default:False) – Configure the features to include. Can be a feature name or a list of such names. If"queryset", infers the features used within the current queryset. Only available forArtifact,Record, andRun.limit (
int, default:100) – Maximum number of rows to display. IfNone, includes all results.order_by – Field name to order the records by. Prefix with ‘-’ for descending order. Defaults to ‘-id’ to get the most recent records. This argument is ignored if the queryset is already ordered or if the specified field does not exist.
- Return type:
DataFrame
Examples
Include the name of the creator:
ln.Record.to_dataframe(include="created_by__name"])
Include features:
ln.Artifact.to_dataframe(include="features")
Include selected features:
ln.Artifact.to_dataframe(features=["cell_type_by_expert", "cell_type_by_model"])
- classmethod search(string, *, field=None, limit=20, case_sensitive=False)¶
Search.
- Parameters:
string (
str) – The input string to match against the field ontology values.field (
str|DeferredAttribute|None, default:None) – The field or fields to search. Search all string fields by default.limit (
int|None, default:20) – Maximum amount of top results to return.case_sensitive (
bool, default:False) – Whether the match is case sensitive.
- Return type:
- Returns:
A sorted
DataFrameof search results with a score in columnscore. Ifreturn_querysetisTrue.QuerySet.
See also
filter()lookup()Examples
records = ln.Record.from_values(["Label1", "Label2", "Label3"], field="name").save() ln.Record.search("Label2")
- classmethod lookup(field=None, return_field=None)¶
Return an auto-complete object for a field.
- Parameters:
field (
str|DeferredAttribute|None, default:None) – The field to look up the values for. Defaults to first string field.return_field (
str|DeferredAttribute|None, default:None) – The field to return. IfNone, returns the whole record.keep – When multiple records are found for a lookup, how to return the records. -
"first": return the first record. -"last": return the last record. -False: return all records.
- Return type:
NamedTuple- Returns:
A
NamedTupleof lookup information of the field values with a dictionary converter.
See also
search()Examples
Lookup via auto-complete on
.:import bionty as bt bt.Gene.from_source(symbol="ADGB-DT").save() lookup = bt.Gene.lookup() lookup.adgb_dt
Look up via auto-complete in dictionary:
lookup_dict = lookup.dict() lookup_dict['ADGB-DT']
Look up via a specific field:
lookup_by_ensembl_id = bt.Gene.lookup(field="ensembl_gene_id") genes.ensg00000002745
Return a specific field value instead of the full record:
lookup_return_symbols = bt.Gene.lookup(field="ensembl_gene_id", return_field="symbol")
Methods¶
- replace(data, run=None, format=None)¶
Replace the artifact content in storage without making a new version.
Note: If you want to create a new version, do not use the
.replace()method but rather anyArtifactconstructor.- Parameters:
data (lamindb.core.types.UPathStr |
DataFrame|AnnData|MuData) – A file path or in-memory dataset object like aDataFrame,AnnData,MuData, orSpatialData.run (
Run|bool|None, default:None) –Run | bool | None = NoneThe run that creates the artifact. IfFalse, suppress tracking the run. IfNone, infer the run from the global run context.format (
str|None, default:None) –str | None = NoneThe format of the data to write into storage. IfNone, infer the format from the data.
- Return type:
None
Example
Query a text file and replace its content:
artifact = ln.Artifact.get(key="my_file.txt") artifact.replace("./my_new_file.txt") artifact.save()
Note that you need to call
.save()to persist the changes in storage.
- open(mode='r', engine='pyarrow', is_run_input=None, **kwargs)¶
Open a dataset for streaming.
Works for the following object types (storage formats):
DataFrame(.parquet,.csv,.ipcfiles or directories with such files)AnnData(.h5ad,.zarr)SpatialData(.zarr)tiledbsoma(.tiledbsoma)generic arrays (
.h5,.zarr)
- Parameters:
mode (str, default:
'r') – can be"r"or"w"(write mode) fortiledbsomastores,"r"or"r+"forAnnDataorSpatialDatazarrstores, otherwise should be always"r"(read-only mode).engine (Literal[‘pyarrow’, ‘polars’], default:
'pyarrow') – Which module to use for lazy loading of a dataframe frompyarroworpolarscompatible formats. This has no effect if the artifact is not a dataframe, i.e. if it is anAnnData,hdf5,zarr,tiledbsomaobject etc.is_run_input (bool | None, default:
None) – Whether to track this artifact as run input.**kwargs – Keyword arguments for the accessor, i.e.
h5pyorzarrconnection,pyarrow.dataset.dataset,polars.scan_*function.
- Return type:
PyArrowDataset | Iterator[PolarsLazyFrame] | AnnDataAccessor | SpatialDataAccessor | BackedAccessor | SOMACollection | SOMAExperiment | SOMAMeasurement
- Returns:
Streaming accessors, in particular, a
pyarrow.dataset.Datasetobject, a context manager yielding a polars.LazyFrame, and objects of typeAnnDataAccessor,SpatialDataAccessor,BackedAccessor,tiledbsoma.Collection,tiledbsoma.Experiment,tiledbsoma.Measurement.
Examples
Open a
DataFrame-like artifact viapyarrow.dataset.Dataset:artifact = ln.Artifact.get(key="sequences/mydataset.parquet") artifact.open() #> pyarrow._dataset.FileSystemDataset
Open a
DataFrame-like artifact via polars.LazyFrame:artifact = ln.Artifact.get(key="sequences/mydataset.parquet") with artifact.open(engine="polars") as df: # use the `polars.LazyFrame` object similar to a `DataFrame` object
Open an
AnnData-like artifact viaAnnDataAccessor:import lamindb as ln artifact = ln.Artifact.get(key="scrna/mydataset.h5ad") with artifact.open() as adata: # use the `AnnDataAccessor` similar to an `AnnData` object
For more examples and background, see guide: Stream datasets from storage .
- load(*, is_run_input=None, mute=False, **kwargs)¶
Cache artifact in local cache and then load it into memory.
See:
loaders.- Parameters:
is_run_input (bool | None, default:
None) – Whether to track this artifact as run input.mute (bool, default:
False) – Silence logging of caching progress.**kwargs – Keyword arguments for the loader.
- Return type:
pd.DataFrame | ScverseDataStructures | dict[str, Any] | list[Any] | UPathStr | None
Examples
Load a
DataFrame-like artifact:df = artifact.load()
Load an
AnnData-like artifact:adata = artifact.load()
- cache(*, is_run_input=None, mute=False, **kwargs)¶
Download cloud artifact to local cache.
Follows synching logic: only caches an artifact if it’s outdated in the local cache.
Returns a path to a locally cached on-disk object (say a
.jpgfile).- Parameters:
mute (
bool, default:False) – Silence logging of caching progress.is_run_input (
bool|None, default:None) – Whether to track this artifact as run input.
- Return type:
Path
Example
Sync the artifact from the cloud and return the local path to the cached file:
artifact.cache() #> PosixPath('/home/runner/work/Caches/lamindb/lamindata/pbmc68k.h5ad')
- delete(permanent=None, storage=None, using_key=None)¶
Trash or permanently delete.
A first call to
.delete()puts an artifact into the trash (setsbranch_idto-1). A second call permanently deletes the artifact.For an
artifactthat has multiple versions and for whichartifact.overwrite_versions is True, the default behavior for folders, deleting a non-latest version will not delete the underlying storage unlessstorage=Trueis passed. Deleting the latest version will delete all versions.- Parameters:
permanent (
bool|None, default:None) – Permanently delete the artifact (skip trash).storage (
bool|None, default:None) – Indicate whether you want to delete the artifact in storage.
- Return type:
None
Examples
Delete a single file artifact:
import lamindb as ln artifact = ln.Artifact.get(key="some.csv") artifact.delete() # delete a single file artifact
Delete an old version of a folder-like artifact:
artifact = ln.Artifact.filter(key="folder.zarr", is_latest=False).first() artiact.delete() # delete an old version, the data will not be deleted
Delete all versions of a folder-like artifact:
artifact = ln.Artifact.get(key="folder.zarr". is_latest=True) artifact.delete() # delete all versions, the data will be deleted or prompted for deletion.
- save(upload=None, transfer='record', **kwargs)¶
Save to database & storage.
- Parameters:
upload (
bool|None, default:None) – Trigger upload to cloud storage in instances with hybrid storage mode.transfer (
Literal['record','annotations'], default:'record') – In case artifact was queried on a different instance, dictates behavior of transfer. If “record”, only the artifact record is transferred to the current instance. If “annotations”, also the annotations linked in the source instance are transferred.
- Return type:
See also
Example
Save a file-like artifact after creating it with the default constructor
Artifact():import lamindb as ln artifact = ln.Artifact("./myfile.csv", key="myfile.parquet").save()
- view_lineage(with_children=True, return_graph=False)¶
View data lineage graph.
- Return type:
Digraph|None
- restore()¶
Restore from trash onto the main branch.
Does not restore descendant objects if the object is
HasTypewithis_type = True.- Return type:
None
- classmethod describe(include=None)¶
Describe record including relations.
- Parameters:
return_str (
bool, default:False) – Return a string instead of printing.include (
None|Literal['comments'], default:None) – Include additional content. Use"comments"to display readme and comment blocks.
- Return type:
None|str
- refresh_from_db(using=None, fields=None, from_queryset=None)¶
Reload field values from the database.
By default, the reloading happens from the database this instance was loaded from, or by the read router if this instance wasn’t loaded from any database. The using parameter will override the default.
Fields can be used to specify which fields to reload. The fields should be an iterable of field attnames. If fields is None, then all non-deferred fields are reloaded.
When accessing deferred fields of an instance, the deferred loading of the field will call this method.