Work with sheets  ¶
¶
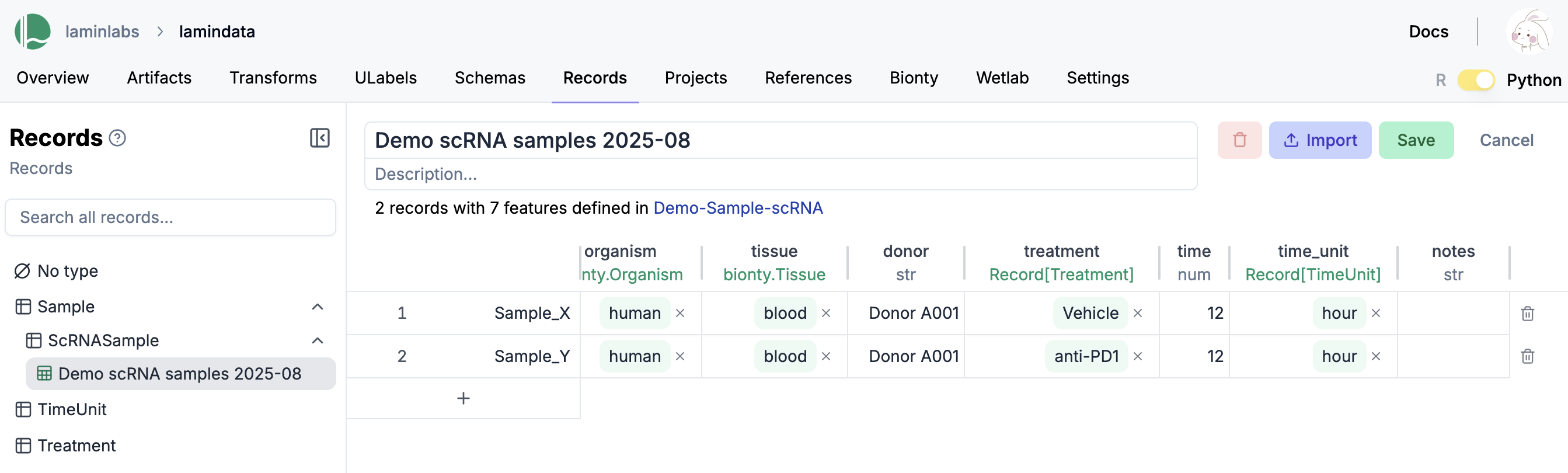
The hub offers a spreadsheet-like experience for managing metadata based on LaminDB’s Record registry.
Create a sheet¶
Create or select a sheet type on the left navbar. Example
Organize your sheets using types, similar to creating folders that contain different groups of related sheets. This hierarchical structure is visualized in the left navigation panel—click the
+button to create new sheet types and build your organizational taxonomy.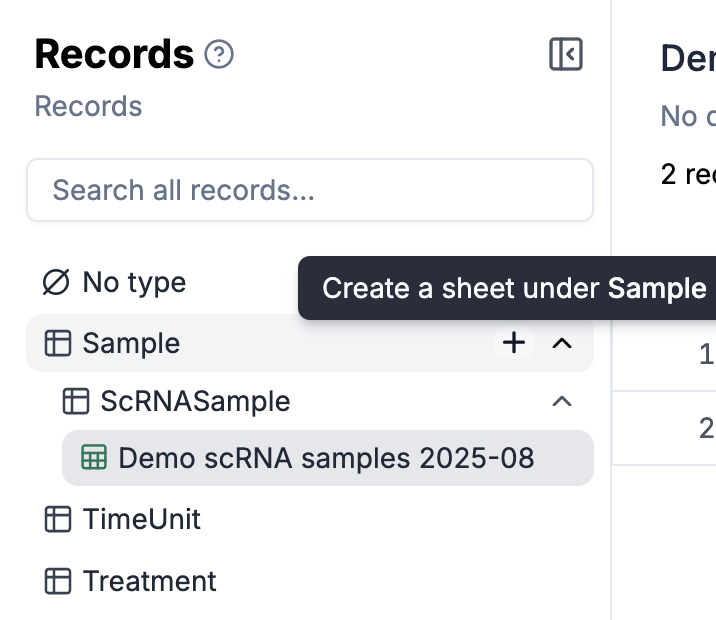
Select the sheet type you want to create sheet under.
Click on “Edit” to add edit rows in the sheet.
Each value in the sheet becomes a selectable option in dropdown menus.
You can link columns in one sheet to another sheet or registry by specifying the appropriate data type. This creates relational connections that maintain data integrity and enable powerful cross-referencing.
In the example shown, the
time_unitcolumn points to the TimeUnit sheet, which defines the permissible values for this field. This relationship ensures that only valid time units can be selected.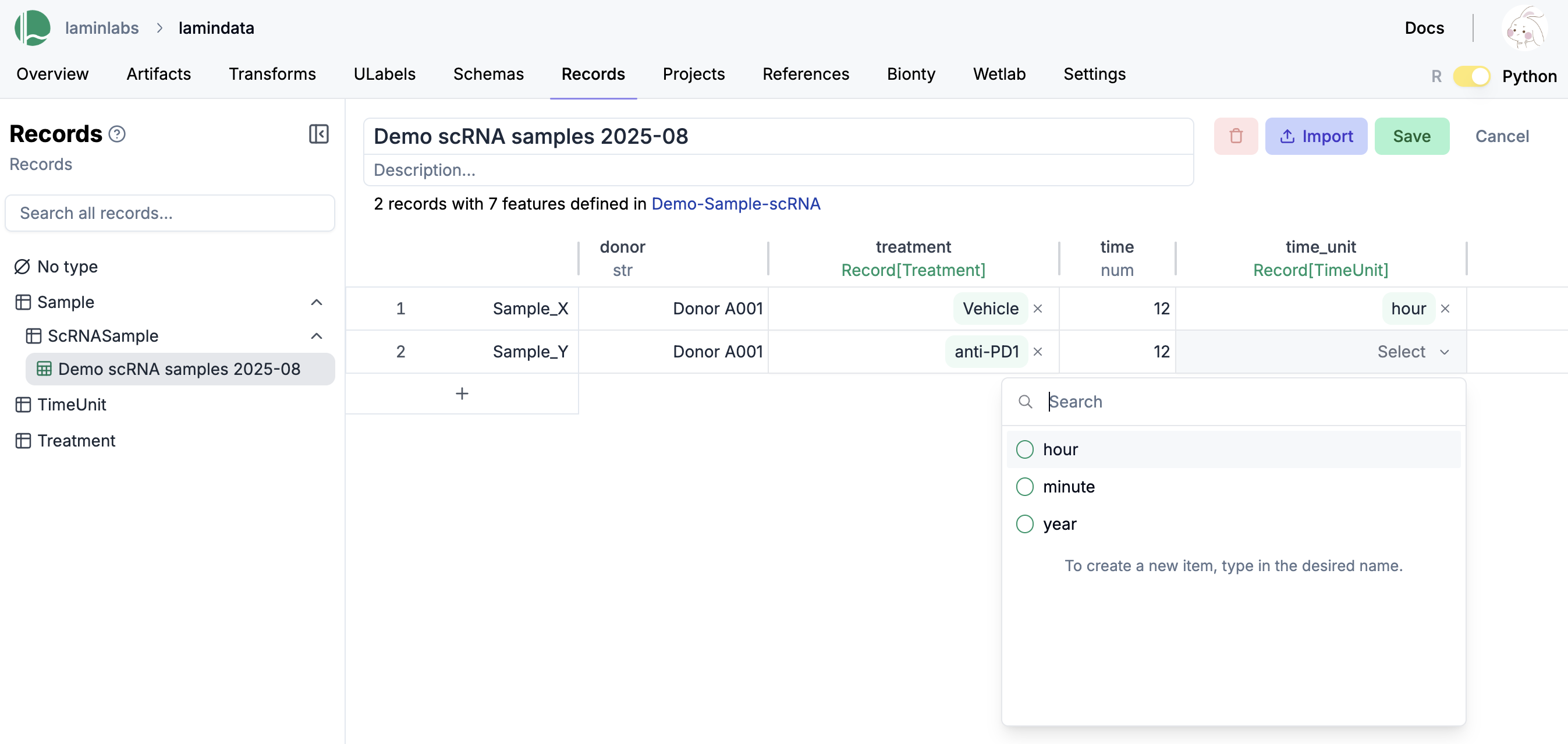
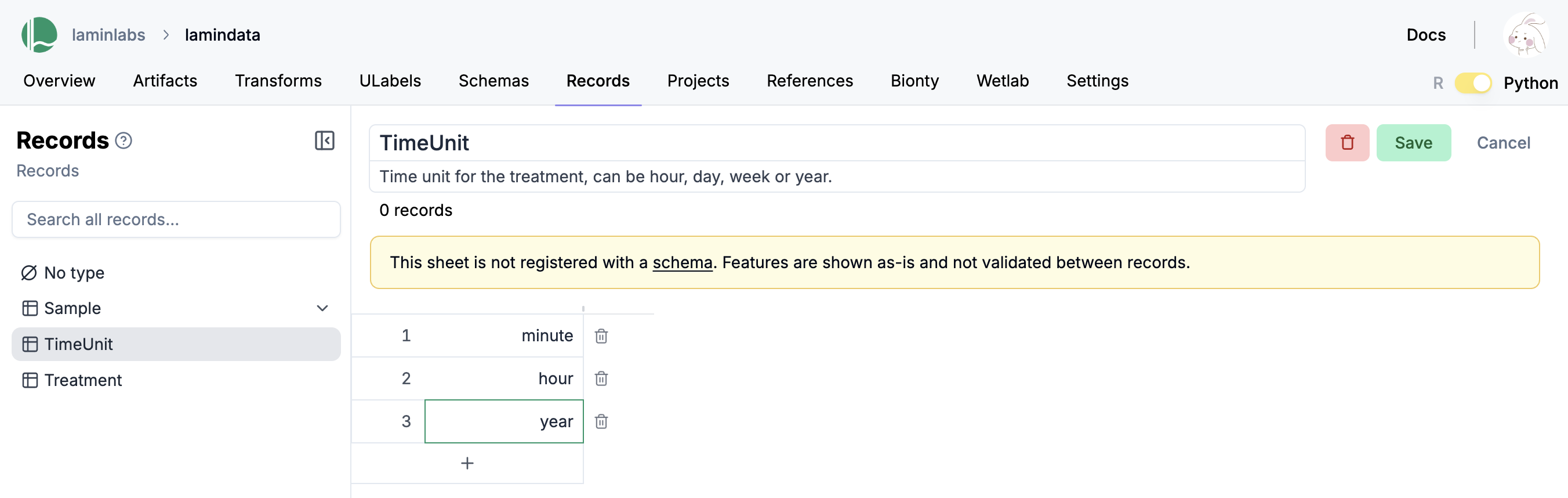
Column relationships include registry links to predefined registries like TimeUnit or Treatment, ontology references that connect to biological ontologies (bionty.Organism, bionty.Tissue), cross-sheet references that link to records in other custom sheets, and enum constraints that restrict values to predefined lists.
Enforcing schemas on sheets¶
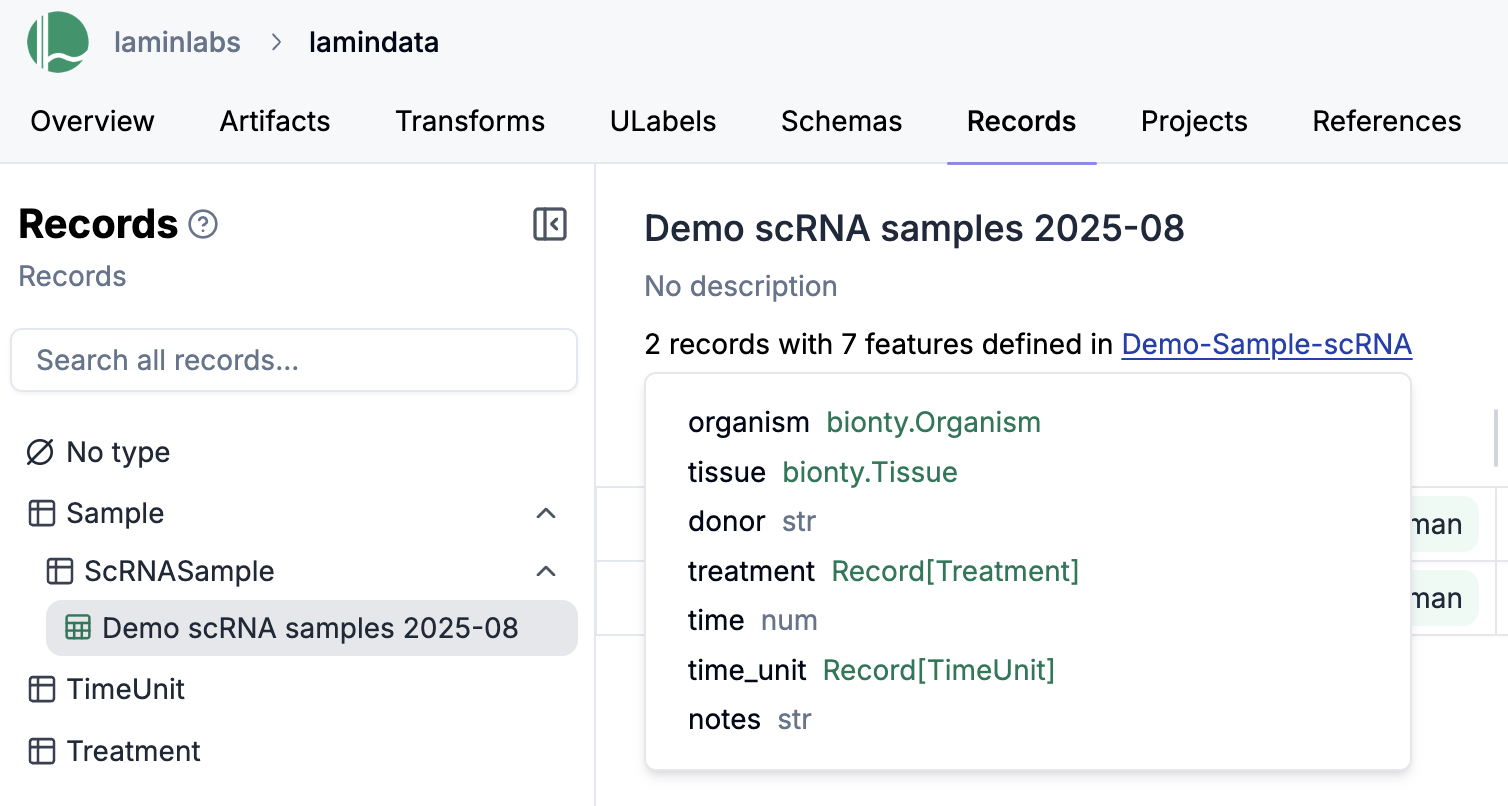
When you register a sheet with a schema, you create a standardized template that ensures consistency across all records.
Schema-enfored sheets display field definitions in the headers, showing both field names and their corresponding data types. This provides immediate visibility into the expected data structure.
Export sheets¶
Click on “Export to Artifact” to save the sheet as a CSV artifact, this will then allow you to download via UI or load the sheets using LaminDB.