lamindb.Storage  ¶
¶
- class lamindb.Storage(root: str, *, description: str | None = None, space: Space | None = None, host: str | None = None)¶
Bases:
SQLRecord,TracksRun,TracksUpdatesStorage locations of artifacts such as local directories or S3 buckets.
A storage location is either a directory (local or a folder in the cloud) or an entire S3/GCP bucket.
A storage location is written to by at most one LaminDB instance: the location’s writing instance. Some locations are not managed with LaminDB and, hence, do not have a writing instance.
Writable vs. read-only storage locations
The
instance_uidfield ofStoragedefines its writing instance. Only if a storage location’sinstance_uidmatches your current instance’suid(ln.settings.instance_uid), you can write to it. All other storage locations are read-only in your current instance.Here is an example (source).
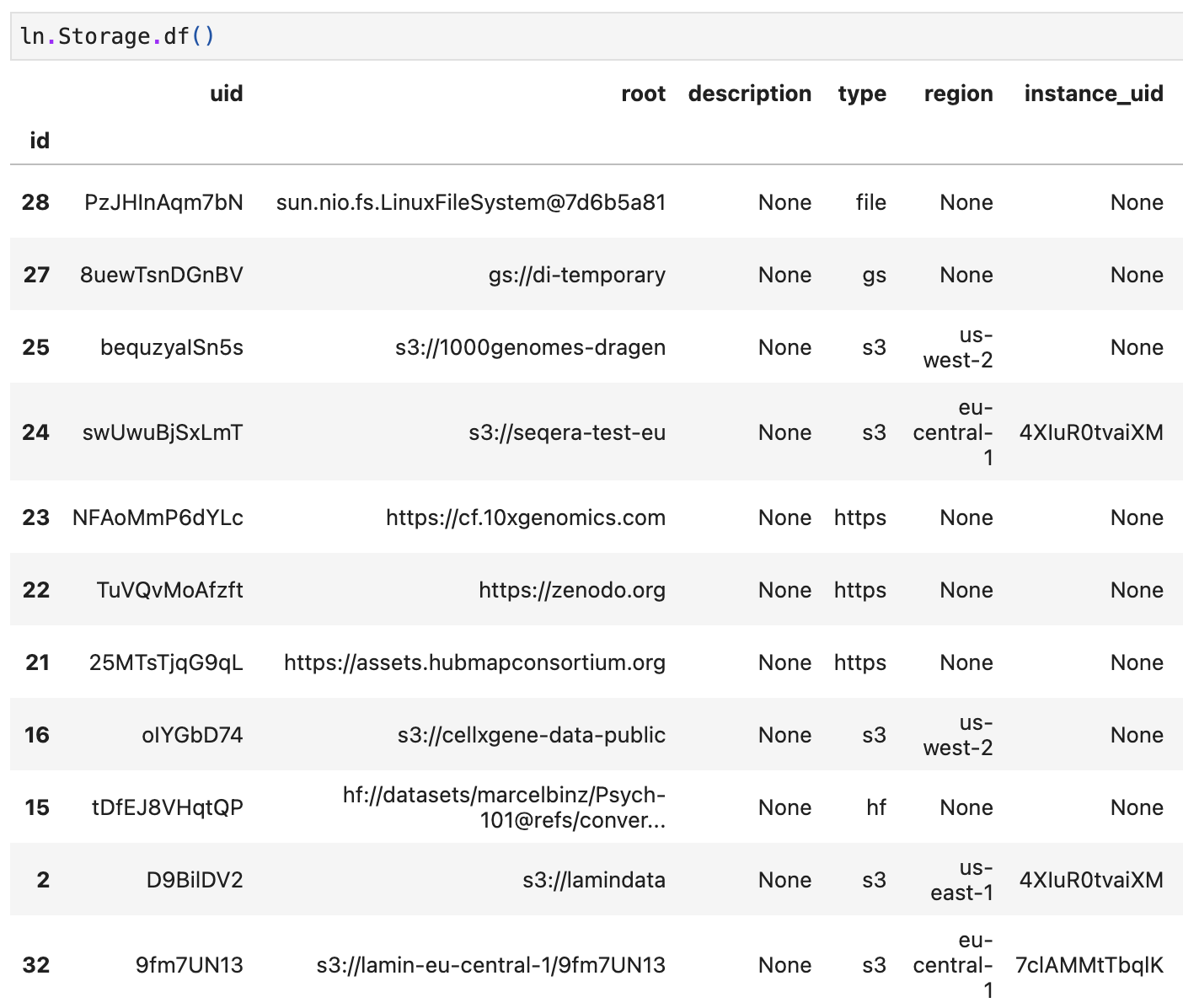
Some storage locations are not written to by any LaminDB instance, hence, their
instance_uidisNone.Managing access to storage locations across instances
You can manage access through LaminHub’s fine-grained access management or through AWS policies that you attach to your S3 bucket.
To enable access management via LaminHub, head over to
https://lamin.ai/{account}/infrastructure. By clicking the green button that says “Connect S3 bucket”, your collaborators will access data based on their LaminHub permissions. Manage access permissions has more details.
By default, a storage location inherits the access permissions of its instance. If you want to further restrict access to a storage location, you can move it into a space:
space = ln.Space.get(name="my-space") storage_loc = ln.Storage.get(root="s3://my-storage-location") storage_loc.space = space storage_loc.save()
If you don’t want to store data in the cloud, you can use local storage locations: Keep artifacts local in a cloud instance .
- Parameters:
root –
strThe root path of the storage location, e.g.,"./mydir","s3://my-bucket","s3://my-bucket/myfolder","gs://my-bucket/myfolder","/nfs/shared/datasets/genomics","/weka/shared/models/", …description –
str | None = NoneAn optional description.space –
Space | None = NoneA space to restrict access permissions to the storage location.host –
str | None = NoneFor local storage locations, a globally unique identifier for the physical machine/server hosting the storage. This distinguishes storage locations that may have the same local path but exist on different servers, e.g."my-institute-cluster-1","my-server-abcd".
See also
lamindb.core.Settings.storageCurrent default storage location of your compute session for writing artifacts.
StorageSettingsStorage settings.
- Keep artifacts local in a cloud instance
Avoid storing artifacts in the cloud, but keep them on local infrastructure.
Examples
When you create a LaminDB instance, you configure its default storage location via
--storage:lamin init --storage ./mydatadir # or "s3://my-bucket/myfolder", "gs://my-bucket/myfolder", ...
View the current default storage location for writing artifacts:
import lamindb as ln ln.settings.storage
Create a new cloud storage location:
ln.Storage(root="s3://our-bucket/our-folder").save()
Create a new local storage location:
ln.Storage(root="/dir/our-shared-dir", host="our-server-123").save()
Globally switch to another storage location:
ln.settings.storage = "/dir/our-shared-dir" # or "s3://our-bucket/our-folder", "gs://our-bucket/our-folder", ...
Or if you’re operating in
keep-artifacts-localmode (Keep artifacts local in a cloud instance ):ln.settings.local_storage = "/dir/our-other-shared-dir"
View all storage locations used in your LaminDB instance:
ln.Storage.to_dataframe()
Notes
What is the
.lamindb/directory inside a storage location?It stores all artifacts that are ingested through
lamindb, indexed by the artifactuid. This means you don’t have to worry about renaming or moving files, as this all happens on the database level.Existing artifacts are typically stored in hierarchical structures with semantic folder names. Instead of copying such artifacts into
.lamindb/upon calls ofArtifact("legacy_path").save(), LaminDB registers them with the semantickeyrepresenting the relative path within the storage location. These artifacts are marked withartifact._key_is_virtual = Falseand treated correspondingly.There is only a single
.lamindb/directory per storage location.What should I do if I want to bulk migrate all artifacts to another storage?
Currently, you can only achieve this manually and you should be careful with it.
Copy or move artifacts into the desired new storage location
Adapt the corresponding record in the {class}`~lamindb.Storage` registry by setting the
rootfield to the new locationIf your LaminDB storage location is connected to the hub, you also need to update the storage record on the hub
Attributes¶
- property host: str | None¶
Host identifier for local storage locations.
Is
Nonefor locations withtype != "local".A globally unique user-defined host identifier (cluster, server, laptop, etc.).
Simple fields¶
- uid: str¶
Universal id, valid across DB instances.
- root: str¶
Root path of storage (cloud or local path).
- description: str | None¶
A description.
- type: StorageType¶
Can be “local” vs. “s3” vs. “gs”. Is auto-detected from the format of the
rootpath.
- region: str | None¶
Storage region for cloud storage locations. Host identifier for local storage locations.
- instance_uid: str | None¶
The writing instance.
Only the LaminDB instance with this
uidcan write to this storage location. This instance also governs the access permissions of the storage location unless the location is moved into a space.
- is_locked: bool¶
Whether the object is locked for edits.
- created_at: datetime¶
Time of creation of record.
- updated_at: datetime¶
Time of last update to record.
Relational fields¶
- created_on¶
Class methods¶
- classmethod filter(*queries, **expressions)¶
Query records.
- Parameters:
queries – One or multiple
Qobjects.expressions – Fields and values passed as Django query expressions.
- Return type:
See also
Guide: Query & search registries
Django documentation: Queries
Examples
>>> ln.Project(name="my label").save() >>> ln.Project.filter(name__startswith="my").to_dataframe()
- classmethod get(idlike=None, **expressions)¶
Get a single record.
- Parameters:
idlike (
int|str|None, default:None) – Either a uid stub, uid or an integer id.expressions – Fields and values passed as Django query expressions.
- Raises:
lamindb.errors.ObjectDoesNotExist – In case no matching record is found.
- Return type:
See also
Guide: Query & search registries
Django documentation: Queries
Examples
record = ln.Record.get("FvtpPJLJ") record = ln.Record.get(name="my-label")
- classmethod to_dataframe(include=None, features=False, limit=100)¶
Evaluate and convert to
pd.DataFrame.By default, maps simple fields and foreign keys onto
DataFramecolumns.Guide: Query & search registries
- Parameters:
include (
str|list[str] |None, default:None) – Related data to include as columns. Takes strings of form"records__name","cell_types__name", etc. or a list of such strings. ForArtifact,Record, andRun, can also pass"features"to include features with data types pointing to entities in the core schema. If"privates", includes private fields (fields starting with_).features (
bool|list[str], default:False) – Configure the features to include. Can be a feature name or a list of such names. If"queryset", infers the features used within the current queryset. Only available forArtifact,Record, andRun.limit (
int, default:100) – Maximum number of rows to display. IfNone, includes all results.order_by – Field name to order the records by. Prefix with ‘-’ for descending order. Defaults to ‘-id’ to get the most recent records. This argument is ignored if the queryset is already ordered or if the specified field does not exist.
- Return type:
DataFrame
Examples
Include the name of the creator:
ln.Record.to_dataframe(include="created_by__name"])
Include features:
ln.Artifact.to_dataframe(include="features")
Include selected features:
ln.Artifact.to_dataframe(features=["cell_type_by_expert", "cell_type_by_model"])
- classmethod search(string, *, field=None, limit=20, case_sensitive=False)¶
Search.
- Parameters:
string (
str) – The input string to match against the field ontology values.field (
str|DeferredAttribute|None, default:None) – The field or fields to search. Search all string fields by default.limit (
int|None, default:20) – Maximum amount of top results to return.case_sensitive (
bool, default:False) – Whether the match is case sensitive.
- Return type:
- Returns:
A sorted
DataFrameof search results with a score in columnscore. Ifreturn_querysetisTrue.QuerySet.
See also
filter()lookup()Examples
records = ln.Record.from_values(["Label1", "Label2", "Label3"], field="name").save() ln.Record.search("Label2")
- classmethod lookup(field=None, return_field=None)¶
Return an auto-complete object for a field.
- Parameters:
field (
str|DeferredAttribute|None, default:None) – The field to look up the values for. Defaults to first string field.return_field (
str|DeferredAttribute|None, default:None) – The field to return. IfNone, returns the whole record.keep – When multiple records are found for a lookup, how to return the records. -
"first": return the first record. -"last": return the last record. -False: return all records.
- Return type:
NamedTuple- Returns:
A
NamedTupleof lookup information of the field values with a dictionary converter.
See also
search()Examples
Lookup via auto-complete on
.:import bionty as bt bt.Gene.from_source(symbol="ADGB-DT").save() lookup = bt.Gene.lookup() lookup.adgb_dt
Look up via auto-complete in dictionary:
lookup_dict = lookup.dict() lookup_dict['ADGB-DT']
Look up via a specific field:
lookup_by_ensembl_id = bt.Gene.lookup(field="ensembl_gene_id") genes.ensg00000002745
Return a specific field value instead of the full record:
lookup_return_symbols = bt.Gene.lookup(field="ensembl_gene_id", return_field="symbol")
Methods¶
- save(*args, **kwargs)¶
Save the storage record.
- delete(permanent=None)¶
Delete the storage location.
This errors in case the storage location is not empty.
Unlike other
SQLRecord-based registries, this does not move the storage record into the trash.- Parameters:
permanent (
bool|None, default:None) –Falseraises an error, as soft delete is impossible.- Return type:
None
- restore()¶
Restore from trash onto the main branch.
Does not restore descendant objects if the object is
HasTypewithis_type = True.- Return type:
None
- classmethod describe(include=None)¶
Describe record including relations.
- Parameters:
return_str (
bool, default:False) – Return a string instead of printing.include (
None|Literal['comments'], default:None) – Include additional content. Use"comments"to display readme and comment blocks.
- Return type:
None|str
- refresh_from_db(using=None, fields=None, from_queryset=None)¶
Reload field values from the database.
By default, the reloading happens from the database this instance was loaded from, or by the read router if this instance wasn’t loaded from any database. The using parameter will override the default.
Fields can be used to specify which fields to reload. The fields should be an iterable of field attnames. If fields is None, then all non-deferred fields are reloaded.
When accessing deferred fields of an instance, the deferred loading of the field will call this method.